Reaction Types
Help Questions
AP Chemistry › Reaction Types
Which of the following is what determines the strength of an acid?
The Ka
The Kb
Its physical state
How many bonds the central atom makes
Electronegativity values
Explanation
The Ka is the acid dissociation constant, and thus it is what determines how strong the acid is. Stronger acids dissociate to a greater extent and produce lower pH values.
Consider the following reaction:
What is the oxidizing agent, and what is the reducing agent?
Silver is the oxidizing agent and copper is the reducing agent
Silver is the reducing agent and copper is the oxidizing agent
Silver is the oxidizing agent and there is no reducing agent
No redox chemistry occurs
Silver is the reducing agent and there is no oxidizing agent
Explanation
Let's break down the reaction into two separate reactions:

We can see that copper loses electrons, while silver gains electrons. Recall that oxidation is loss and reduction is gain, with regard to electrons. Copper is oxidized and silver is reduced.
However, this question asks for the oxidizing agent and reducing agent. Recall that the oxidizing agent is reduced, while the reducing agent is oxidized. Since copper is oxidized, it is the reducing agent. Similarly, since silver is reduced, it is the oxidizing agent.
In the following reaction, which compound is being oxidized?
Copper
Sulfur
Hydrogen
Nitrate
No oxidation takes place
Explanation
Hydrogen doesn't change. Cu2+ doesn't change (partnered with S2- then with SO42-). Sulfur goes from S2- and S6+(paired with 6 O2- with a 2– charge), showing an oxidation. Nitrogen goes from N5+ to N2+ meaning it was reduced.
In the following reaction, which compound is being oxidized?
Copper
Sulfur
Hydrogen
Nitrate
No oxidation takes place
Explanation
Hydrogen doesn't change. Cu2+ doesn't change (partnered with S2- then with SO42-). Sulfur goes from S2- and S6+(paired with 6 O2- with a 2– charge), showing an oxidation. Nitrogen goes from N5+ to N2+ meaning it was reduced.
How many electrons are involved in the following reaction?
1 e-
2 e-
4 e-
5 e-
10 e-
Explanation
The common factor between 2 e- and 5 e- is 10. Therefore the number of electrons involved is 10 e-.
The following ReDox reaction takes place in acidic solution:
Fe2+ + Cr2O72– → Fe3+ + Cr3+
What is the sum of coefficients in this redox reaction?
36
35
34
33
37
Explanation
When you balance the redox reaction in acidic conditons, there are 6Fe2+, 1 Cr2O72–, 14 H+, 6 Fe3+, 2 Cr3+, and 7 H2O. Don't forget to add the 1 in front of the Cr2O72–
Which of the following is what determines the strength of an acid?
The Ka
The Kb
Its physical state
How many bonds the central atom makes
Electronegativity values
Explanation
The Ka is the acid dissociation constant, and thus it is what determines how strong the acid is. Stronger acids dissociate to a greater extent and produce lower pH values.
If you have a solution that consists of a monoprotic acid (HA), with a pKa of 4.1 and at a pH of 5.8, what is the predominant species present?
HA
A-
H2A+
H3O+
Equal amounts of acid and conjugate base are present.
Explanation
Since pH > pKA, the deprotonated form of the acid is predominant.
Determine the pH of a solution that is 
Explanation
Since 

Thus, ![[H_3O^+]=0.40M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668813/gif.latex)
Recall how to find the pH of a solution:
Plug in the given hydronium ion concentration to find the pH of the given solution.
Remember to maintain the correct number of significant figures.
Which of the following will increase the pH of an 
I. Removing carbonic acid
II. Adding sodium bicarbonate
Both I and II
I only
II only
Neither of these options
Explanation
To answer this question we need to look at the reaction below:
An increase in the pH will result in a decrease in the concentration of hydrogen ions (
![[H_3O^+]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/324540/gif.latex)
Removing carbonic acid will decrease the concentration of 
![[H_3O^+]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/324542/gif.latex)
Recall that salts like sodium bicarbonate, or 


![[H_3O^+]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/324546/gif.latex)





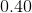



![\text{pH}=-\log([H_3O^+])](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668814/gif.latex)

