Macromolecule Structures and Functions - Biochemistry
Card 1 of 788
Phosphoglucomutase is an enzyme seen in glycogen breakdown. It is responsible for converting glucose-1-phosphate ( ) to glucose-6-phosphate (
) to glucose-6-phosphate (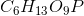 ).
).
Based on this action, to which enzyme class does phosphoglucomutase belong?
Phosphoglucomutase is an enzyme seen in glycogen breakdown. It is responsible for converting glucose-1-phosphate (
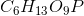
Based on this action, to which enzyme class does phosphoglucomutase belong?
Tap to reveal answer
Phosphoglucomutase is responsible for altering the position of the phosphate on the glucose from the "1" position to the "6" position. However, notice how the molecular formula for the product and the substrate are the same. Enzymes that rearrange the structure of a molecule in this manner are referred to as isomerase enzymes.
Phosphoglucomutase is responsible for altering the position of the phosphate on the glucose from the "1" position to the "6" position. However, notice how the molecular formula for the product and the substrate are the same. Enzymes that rearrange the structure of a molecule in this manner are referred to as isomerase enzymes.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the role of xanthine oxidase?
I. The enzyme xanthine oxidase converts hypoxanthine to xanthine and, also, xanthine to uric acid.
II. Xanthine oxidase is involved in purine (nucleotides like adenine, guanine) degradation.
III. In diseases where there is a high production of purines, the enzyme's products (uric acid) can cause gout.
IV. Gout medication is designed to target xanthine oxidase.
What is the role of xanthine oxidase?
I. The enzyme xanthine oxidase converts hypoxanthine to xanthine and, also, xanthine to uric acid.
II. Xanthine oxidase is involved in purine (nucleotides like adenine, guanine) degradation.
III. In diseases where there is a high production of purines, the enzyme's products (uric acid) can cause gout.
IV. Gout medication is designed to target xanthine oxidase.
Tap to reveal answer
Xanthine oxidase is an enzyme important in purine catabolism. Nucleotides from DNA degradation are metabolized to uric acid by xanthine oxidase.In diseases with high levels of nucleotide production, uric acid levels are also high and produce symptoms of gout (uric acid is deposited abnormally in tissues). Gout is treated with inhibitors of xanthine oxidase such as allopurinol, reducing the levels of uric acid and the symptoms of gout.
Xanthine oxidase is an enzyme important in purine catabolism. Nucleotides from DNA degradation are metabolized to uric acid by xanthine oxidase.In diseases with high levels of nucleotide production, uric acid levels are also high and produce symptoms of gout (uric acid is deposited abnormally in tissues). Gout is treated with inhibitors of xanthine oxidase such as allopurinol, reducing the levels of uric acid and the symptoms of gout.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which statement concerning DNA methylation in mammals is false?
Which statement concerning DNA methylation in mammals is false?
Tap to reveal answer
Unmethylated cytosine spontaneously deaminates to uracil. Over time, methylated cytosine is spontaneously deaminated to thymine. Random deamination of methylcytosines causes mutation, creating hot spots. The vast majority of DNA methylations in mammals occurs at CpG (cytosine-phospate-guanine) sites.
Unmethylated cytosine spontaneously deaminates to uracil. Over time, methylated cytosine is spontaneously deaminated to thymine. Random deamination of methylcytosines causes mutation, creating hot spots. The vast majority of DNA methylations in mammals occurs at CpG (cytosine-phospate-guanine) sites.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following describes a mutation in which a segment of DNA detaches from a chromosome and reattaches to another chromosome?
Which of the following describes a mutation in which a segment of DNA detaches from a chromosome and reattaches to another chromosome?
Tap to reveal answer
A null mutation is one that deactivates a gene entirely. Point mutations are those that occur within a single, small site in a gene. Inversion involves the reversal of orientation of a DNA segment. Deletion occurs when a whole part of a chromosome is removed, joining two ends that were far apart. Translocation involves the exchange of genetic material from two chromosomes that are not homologous.
A null mutation is one that deactivates a gene entirely. Point mutations are those that occur within a single, small site in a gene. Inversion involves the reversal of orientation of a DNA segment. Deletion occurs when a whole part of a chromosome is removed, joining two ends that were far apart. Translocation involves the exchange of genetic material from two chromosomes that are not homologous.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Generally, silencing of a gene is accomplished by ?
Generally, silencing of a gene is accomplished by ?
Tap to reveal answer
The silencing of a gene is most often accomplished via methylation of the DNA. The methyl groups are added to the gene's promoter region and thus, the DNA is not read by transcriptional enzymes.
The silencing of a gene is most often accomplished via methylation of the DNA. The methyl groups are added to the gene's promoter region and thus, the DNA is not read by transcriptional enzymes.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
How does methylation cause the silencing of a gene?
How does methylation cause the silencing of a gene?
Tap to reveal answer
In order to silence a gene by methylation, methyl groups are added to the promoter region of DNA. This area is upstream of the coding sequence and is responsible for initiation of transcription. Thus, methylating the promoter region inhibits further transcription of the gene.
In order to silence a gene by methylation, methyl groups are added to the promoter region of DNA. This area is upstream of the coding sequence and is responsible for initiation of transcription. Thus, methylating the promoter region inhibits further transcription of the gene.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following DNA bases can be methylated in the promoter region to silence a gene?
Which of the following DNA bases can be methylated in the promoter region to silence a gene?
Tap to reveal answer
The only two bases that can be methylated are cytosine and adenine.
The only two bases that can be methylated are cytosine and adenine.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Formation of thymine dimers in DNA can lead to conditions such as melanoma when unrepaired. This DNA mutation is primarily caused by .
Formation of thymine dimers in DNA can lead to conditions such as melanoma when unrepaired. This DNA mutation is primarily caused by .
Tap to reveal answer
Alkylating agents and  can also cause cancer, but they lead to methylation and mismatch mutations rather than the formation of pyrimidine dimers.
can also cause cancer, but they lead to methylation and mismatch mutations rather than the formation of pyrimidine dimers.
Alkylating agents and 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which proteins are generally water-soluble?
Which proteins are generally water-soluble?
Tap to reveal answer
In a globular protein, the amino acid chain can twist in a way that polar groups lie at the protein's surface. This allows the protein to interact with water and enhances the protein's solubility in water. This does not occur in fibrous proteins, so fibrous proteins are insoluble in water.
In a globular protein, the amino acid chain can twist in a way that polar groups lie at the protein's surface. This allows the protein to interact with water and enhances the protein's solubility in water. This does not occur in fibrous proteins, so fibrous proteins are insoluble in water.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following is false about actin filaments?
Which of the following is false about actin filaments?
Tap to reveal answer
Actin chain growth occurs at the (+) end of the chain, and nucleotide hydrolysis promotes dissociation of actin chains. 2 microfilaments of G-actin monomers make 1 filament of F-actin. However, actin filament assembly is powered by ATP, not GTP.
Actin chain growth occurs at the (+) end of the chain, and nucleotide hydrolysis promotes dissociation of actin chains. 2 microfilaments of G-actin monomers make 1 filament of F-actin. However, actin filament assembly is powered by ATP, not GTP.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
An O-linked glycoprotein has a sugar attached to an oxygen atom on what amino acid(s)?
An O-linked glycoprotein has a sugar attached to an oxygen atom on what amino acid(s)?
Tap to reveal answer
An O-linked glycoprotein is a protein that has a sugar attached to it. It is called O-linked because the sugar is attached to an oxygen atom on either a threonine residue or a serine residue within the protein.
An O-linked glycoprotein is a protein that has a sugar attached to it. It is called O-linked because the sugar is attached to an oxygen atom on either a threonine residue or a serine residue within the protein.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following statements about restriction enzymes is true?
Which of the following statements about restriction enzymes is true?
Tap to reveal answer
Reverse transcriptase synthesizes DNA in the 5' to 3' direction, using RNA as a template (hence it is the reverse of transcription). Restriction enzymes act only on DNA, not RNA, and they can cut bacterial as well as viral DNA—indeed, they can provide protection against viruses—and are found in archaea. Restriction enzymes can recognize specific sequences of nucleotides at restriction sites and cut DNA at these sites. Restriction enzymes do not create covalent bonds between adjacent exons after intron excision, rather this is done by tRNA splicing ligase.
Reverse transcriptase synthesizes DNA in the 5' to 3' direction, using RNA as a template (hence it is the reverse of transcription). Restriction enzymes act only on DNA, not RNA, and they can cut bacterial as well as viral DNA—indeed, they can provide protection against viruses—and are found in archaea. Restriction enzymes can recognize specific sequences of nucleotides at restriction sites and cut DNA at these sites. Restriction enzymes do not create covalent bonds between adjacent exons after intron excision, rather this is done by tRNA splicing ligase.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
If a protein is bonded to ubiquitin, this tells the cell that the protein should be .
If a protein is bonded to ubiquitin, this tells the cell that the protein should be .
Tap to reveal answer
When a protein is damaged, it can be tagged with the molecule, ubiquitin. This signals to the cell that the protein is no longer functioning properly and needs to be degraded.
When a protein is damaged, it can be tagged with the molecule, ubiquitin. This signals to the cell that the protein is no longer functioning properly and needs to be degraded.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
HMGCoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase) is the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. Which of the following are true about the ubiquitination of this enzyme?
I. When cholesterol levels in the cell are high, the reductase binds to insulin-induced gene 1 proteins.
II. Binding to insulin induced gene 1 proteins leads to ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of reductase.
III. Ubiquitination occurs through the binding of the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin to the amino group of a lysine on the reductase.
IV. The enzyme tagged with ubiquitin is recognized by the proteasome where proteolysis occurs.
HMGCoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase) is the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. Which of the following are true about the ubiquitination of this enzyme?
I. When cholesterol levels in the cell are high, the reductase binds to insulin-induced gene 1 proteins.
II. Binding to insulin induced gene 1 proteins leads to ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of reductase.
III. Ubiquitination occurs through the binding of the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin to the amino group of a lysine on the reductase.
IV. The enzyme tagged with ubiquitin is recognized by the proteasome where proteolysis occurs.
Tap to reveal answer
HMGCoA reductase is the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. The reductase is present on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. When levels of its product, cholesterol, are high, the enzyme gets ubiquitinated and degraded in smaller peptides and amino acids. It first binds to insulin-induced gene 1 protein before ubiquitination.
HMGCoA reductase is the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. The reductase is present on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. When levels of its product, cholesterol, are high, the enzyme gets ubiquitinated and degraded in smaller peptides and amino acids. It first binds to insulin-induced gene 1 protein before ubiquitination.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the purpose of the pentose phosphate pathway (also known as the hexose monophosphate shunt or HMS)?
What is the purpose of the pentose phosphate pathway (also known as the hexose monophosphate shunt or HMS)?
Tap to reveal answer
The pentose phosphate pathway (also known as the hexose monophosphate shunt or HMS), mainly serves to produce  for anabolic reduction reactions and ribose-5-phosphate for nucleic acid production.
for anabolic reduction reactions and ribose-5-phosphate for nucleic acid production.
The pentose phosphate pathway (also known as the hexose monophosphate shunt or HMS), mainly serves to produce 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following is an example of a nucleoside?
Which of the following is an example of a nucleoside?
Tap to reveal answer
A nucleoside is composed of both a nitrogenous base as well as a sugar. Cytosine and adenine are just nitrogenous bases. Guanosine monophosphate (or GMP) is also composed of a phosphate group, which designates it as a nucleotide. The only nucleoside is adenosine.
A nucleoside is composed of both a nitrogenous base as well as a sugar. Cytosine and adenine are just nitrogenous bases. Guanosine monophosphate (or GMP) is also composed of a phosphate group, which designates it as a nucleotide. The only nucleoside is adenosine.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which component of a phospholipid imparts a charge upon the macromolecule and therefore makes the head hydrophilic?
Which component of a phospholipid imparts a charge upon the macromolecule and therefore makes the head hydrophilic?
Tap to reveal answer
Phospholipids are amphipathic, meaning they have an end that is hydrophobic (the fatty acid tail) and an end that is hydrophilic (the head). Phosphate groups have a negative charge, thus attracting them to water, and the presence of a phosphate group at the head of a phospholipid makes that head hydrophilic. Glycerol itself polarizes a fatty acid, but the glycerol is located in the head, not the backbone, and is not charged like phosphate.
Phospholipids are amphipathic, meaning they have an end that is hydrophobic (the fatty acid tail) and an end that is hydrophilic (the head). Phosphate groups have a negative charge, thus attracting them to water, and the presence of a phosphate group at the head of a phospholipid makes that head hydrophilic. Glycerol itself polarizes a fatty acid, but the glycerol is located in the head, not the backbone, and is not charged like phosphate.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
In sufficient concentrations, one-tailed phospholipids will form a in solution.
In sufficient concentrations, one-tailed phospholipids will form a in solution.
Tap to reveal answer
The polar head groups and the hydrocarbon tails will separate themselves in such a way that one-tailed phospholipids will form micelles, whereas two-tailed phospholipids will form a bilayer (liposome).
The polar head groups and the hydrocarbon tails will separate themselves in such a way that one-tailed phospholipids will form micelles, whereas two-tailed phospholipids will form a bilayer (liposome).
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following is false about phospholipids?
Which of the following is false about phospholipids?
Tap to reveal answer
Phospholipids have two hydrocarbon tails, and one is indeed usually relatively saturated (has no double bonds) and the other relatively saturated (has double bonds). The degree of saturation, as well as the length, influences membrane fluidity; more cis-double bonds pack together less tightly, and decrease fluidity. In order to minimize free energy, the hydrophobic parts of phospholipids rearrange to refill a bilayer if it happens to break. In water, phospholipids can form a membrane, or a sphere called a micelle in which the hydrophobic tails pack together. Note that the tails are hydrophobic, and the heads are hydrophilic; tails are oriented toward the interior of a bilayered membrane.
Phospholipids have two hydrocarbon tails, and one is indeed usually relatively saturated (has no double bonds) and the other relatively saturated (has double bonds). The degree of saturation, as well as the length, influences membrane fluidity; more cis-double bonds pack together less tightly, and decrease fluidity. In order to minimize free energy, the hydrophobic parts of phospholipids rearrange to refill a bilayer if it happens to break. In water, phospholipids can form a membrane, or a sphere called a micelle in which the hydrophobic tails pack together. Note that the tails are hydrophobic, and the heads are hydrophilic; tails are oriented toward the interior of a bilayered membrane.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Why do phospholipids and glycolipids form bilayers rather than micelles when placed in an aqueous media?
Why do phospholipids and glycolipids form bilayers rather than micelles when placed in an aqueous media?
Tap to reveal answer
Phospholipids and glycolipids have two hydrocarbon chains, whereas free fatty acids only have one. The extra carbon tail, in combination with the unsaturation of these types of lipids (double bonds present) makes them far bulkier than free fatty acids. The extra bulk disallows micelle formation, and bilayers (liposomes) form instead.
Phospholipids and glycolipids have two hydrocarbon chains, whereas free fatty acids only have one. The extra carbon tail, in combination with the unsaturation of these types of lipids (double bonds present) makes them far bulkier than free fatty acids. The extra bulk disallows micelle formation, and bilayers (liposomes) form instead.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →