Rectangular Solids & Cylinders - GMAT Quantitative
Card 1 of 960
What is the length of the diagonal of a cube if its side length is  ?
?
What is the length of the diagonal of a cube if its side length is 
Tap to reveal answer
The diagonal of a cube extends from one of its corners diagonally through the cube to the opposite corner, so it can be thought of as the hypotenuse of a right triangle formed by the height of the cube and the diagonal of its base. First we must find the diagonal of the base, which will be the same as the diagonal of any face of the cube, by applying the Pythagorean theorem:



Now that we know the length of the diagonal of any face on the cube, we can use the Pythagorean theorem again with this length and the height of the cube, whose hypotenuse is the length of the diagonal for the cube:



The diagonal of a cube extends from one of its corners diagonally through the cube to the opposite corner, so it can be thought of as the hypotenuse of a right triangle formed by the height of the cube and the diagonal of its base. First we must find the diagonal of the base, which will be the same as the diagonal of any face of the cube, by applying the Pythagorean theorem:
Now that we know the length of the diagonal of any face on the cube, we can use the Pythagorean theorem again with this length and the height of the cube, whose hypotenuse is the length of the diagonal for the cube:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
 is a cube and face
is a cube and face has an area of
has an area of  . What is the length of diagonal of the cube
. What is the length of diagonal of the cube  ?
?




Tap to reveal answer
To find the diagonal of a cube we can apply the formula  , where
, where  is the length of the diagonal and where
is the length of the diagonal and where  is the length of an edge of the cube.
is the length of an edge of the cube.
Since we are given an area of a face of the cube, we can find the length of an edge simply by taking its square root.

Here the length of an edge is 3.
Thefore the final andwer is  .
.
To find the diagonal of a cube we can apply the formula 


Since we are given an area of a face of the cube, we can find the length of an edge simply by taking its square root.
Here the length of an edge is 3.
Thefore the final andwer is 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the length of the diagonal  of cube
of cube  , knowing that face
, knowing that face  has diagonal equal to
has diagonal equal to  ?
?
What is the length of the diagonal 



Tap to reveal answer
To find the length of the diagonal of the cube, we can apply the formula, however, we firstly need to find the length of an edge, by applying the formula for the diagonal of the square.
 where
where  is the diagonal of face ABCD, and
is the diagonal of face ABCD, and  , the length of one of the side of this square.
, the length of one of the side of this square.
The length of  must be
must be  , which is the length of the edges of the square.
, which is the length of the edges of the square.
Therefore we can now use the formula for the length of the diagonal of the cube:
 , where
, where  is the length of an edge.
is the length of an edge.
Since  , we get the final answer
, we get the final answer  .
.
To find the length of the diagonal of the cube, we can apply the formula, however, we firstly need to find the length of an edge, by applying the formula for the diagonal of the square.



The length of 

Therefore we can now use the formula for the length of the diagonal of the cube:


Since 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
If a cube has a side length of  , what is the length of its diagonal?
, what is the length of its diagonal?
If a cube has a side length of 
Tap to reveal answer
The diagonal of a cube is the hypotenuse of a right triangle whose height is one side and whose base is the diagonal of one of the faces. First we must use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the diagonal of one of the faces, and then we use the theorem again with this value and length of one side of the cube to find the length of its diagonal:



So this is the length of the diagonal of one of the faces, which we plug into the Pythagorean theorem with the length of one side to find the length of the diagonal for the cube:



The diagonal of a cube is the hypotenuse of a right triangle whose height is one side and whose base is the diagonal of one of the faces. First we must use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the diagonal of one of the faces, and then we use the theorem again with this value and length of one side of the cube to find the length of its diagonal:
So this is the length of the diagonal of one of the faces, which we plug into the Pythagorean theorem with the length of one side to find the length of the diagonal for the cube:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A given cube has an edge length of  . What is the length of the diagonal of the cube?
. What is the length of the diagonal of the cube?
A given cube has an edge length of 
Tap to reveal answer
The diagonal  of a cube with an edge length
of a cube with an edge length  can be defined by the equation
can be defined by the equation  . Given
. Given  in this instance,
in this instance,  .
.
The diagonal 




← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A given cube has an edge length of  . What is the length of the diagonal of the cube?
. What is the length of the diagonal of the cube?
A given cube has an edge length of 
Tap to reveal answer
The diagonal  of a cube with an edge length
of a cube with an edge length  can be defined by the equation
can be defined by the equation  . Given
. Given  in this instance,
in this instance,  .
.
The diagonal 




← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A given cube has an edge length of  . What is the length of the diagonal of the cube?
. What is the length of the diagonal of the cube?
A given cube has an edge length of 
Tap to reveal answer
The diagonal  of a cube with an edge length
of a cube with an edge length  can be defined by the equation
can be defined by the equation  . Given
. Given  in this instance,
in this instance,  .
.
The diagonal 




← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The slant height of a pyramid is one and one-half times the perimeter of its square base. The base has sides of length 15 inches. What is the surface area of the pyramid?
The slant height of a pyramid is one and one-half times the perimeter of its square base. The base has sides of length 15 inches. What is the surface area of the pyramid?
Tap to reveal answer
The square base of the pyramid has four sides with length 15 inches, making its perimeter four times that, or 60 inches. The slant height is
 inches.
inches.
Therefore, the area of the base is  square inches.
square inches.
Each of the four lateral triangles has area  square inches.
square inches.
The total surface area is  square inches.
square inches.
The square base of the pyramid has four sides with length 15 inches, making its perimeter four times that, or 60 inches. The slant height is

Therefore, the area of the base is 
Each of the four lateral triangles has area 
The total surface area is 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
In three-dimensional space, the four vertices of a tetrahedron - a solid with four faces - have Cartesian coordinates  .
.
Give the surface area of the tetrahedron.
In three-dimensional space, the four vertices of a tetrahedron - a solid with four faces - have Cartesian coordinates 
Give the surface area of the tetrahedron.
Tap to reveal answer
The tetrahedron looks like this:

 is the origin and
is the origin and  are the other three points, which are 60 units away from the origin on each of the three (perpendicular) axes.
are the other three points, which are 60 units away from the origin on each of the three (perpendicular) axes.
The bottom, front, and left faces are each right triangles whose legs each measure 60. Each face has area
 .
.
The remaining face has three edges each a hypotenuse of one of three congruent right triangles, so its sides are congruent, and it is an equilateral triangle. Its sidelength can be found via the 45-45-90 Theorem to be  , so its area is
, so its area is

The total area is

The tetrahedron looks like this:



The bottom, front, and left faces are each right triangles whose legs each measure 60. Each face has area

The remaining face has three edges each a hypotenuse of one of three congruent right triangles, so its sides are congruent, and it is an equilateral triangle. Its sidelength can be found via the 45-45-90 Theorem to be 
The total area is
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A regular tetrahedron comprises four faces, each of which is an equilateral triangle. If the sum of the lengths of its edges is 120, what is its surface area?
A regular tetrahedron comprises four faces, each of which is an equilateral triangle. If the sum of the lengths of its edges is 120, what is its surface area?
Tap to reveal answer
As shown in the diagram below, a regular tetrahedron has six congruent edges, so each has length  :
:

The area of one face is the area of an equilateral triangle with sidelength 20, which is

The total surface area is four times this, or  .
.
As shown in the diagram below, a regular tetrahedron has six congruent edges, so each has length 

The area of one face is the area of an equilateral triangle with sidelength 20, which is
The total surface area is four times this, or 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →

Refer to the above diagram, which shows a tetrahedron.
 , and
, and  . Give the surface area of the tetrahedron.
. Give the surface area of the tetrahedron.

Refer to the above diagram, which shows a tetrahedron.


Tap to reveal answer
Three of the surfaces of the tetrahedron -  ,
,  , and
, and  - are isosceles right triangles with hypotenuse 30, so by the 45-45-90 Theorem, each leg measures this length divided by
- are isosceles right triangles with hypotenuse 30, so by the 45-45-90 Theorem, each leg measures this length divided by  , or
, or
 .
.
The area of each of these triangles is half the product of its legs, so each area is

Also, the legs are of the same measure among the triangles, the hypotenuses are as well, so the fourth surface  is an equilateral triangle. Its sidelength is
is an equilateral triangle. Its sidelength is  , so we use the equilateral triangle area formula to calculate its area:
, so we use the equilateral triangle area formula to calculate its area:

Add the areas of the faces:

Three of the surfaces of the tetrahedron - 




The area of each of these triangles is half the product of its legs, so each area is
Also, the legs are of the same measure among the triangles, the hypotenuses are as well, so the fourth surface 

Add the areas of the faces:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A regular tetrahedron is a solid with four faces, each of which is an equilateral triangle.
If the lengths of all of the edges of a regular tetrahedron are added, the total length is 120. What is the surface area of the tetrahedron?
A regular tetrahedron is a solid with four faces, each of which is an equilateral triangle.
If the lengths of all of the edges of a regular tetrahedron are added, the total length is 120. What is the surface area of the tetrahedron?
Tap to reveal answer
A tetrahedron looks like this:

The tetrahedron has six edges, and in a regular tetrahedron, they are congruent, so each edge has length  .
.
The area of one face of the tetrahedron, it being an equilateral triangle, can be calulated using the formula

There are four congruent faces, so the total surface area is

Since  , the surface area of the tetrahedron is
, the surface area of the tetrahedron is

A tetrahedron looks like this:

The tetrahedron has six edges, and in a regular tetrahedron, they are congruent, so each edge has length 
The area of one face of the tetrahedron, it being an equilateral triangle, can be calulated using the formula
There are four congruent faces, so the total surface area is
Since 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A regular tetrahedron is a solid with four faces, each of which is an equilateral triangle.
Each edge of a regular tetrahedron has length  . What is the surface area of the tetrahedron?
. What is the surface area of the tetrahedron?
A regular tetrahedron is a solid with four faces, each of which is an equilateral triangle.
Each edge of a regular tetrahedron has length 
Tap to reveal answer
The area of one face of the tetrahedron, it being an equilateral triangle, can be calulated using the formula

There are four congruent faces, so the total surface area is

Since  , the surface area of the tetrahedron is
, the surface area of the tetrahedron is

The area of one face of the tetrahedron, it being an equilateral triangle, can be calulated using the formula
There are four congruent faces, so the total surface area is
Since 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →

Evaluate the surface area of the above tetrahedron.

Evaluate the surface area of the above tetrahedron.
Tap to reveal answer
Three of the faces of the tetrahedron are isosceles right triangles with legs of length 8, and, subsequently, by the 45-45-90 Theorem, hypotenuses of length  . The fourth face, consequently, is an equilateral triangle with three sides of length
. The fourth face, consequently, is an equilateral triangle with three sides of length  .
.
Each of the three right triangle faces has area equal to half the product of its legs , which is
 .
.
The equilateral face has as its area






The sum of the areas of the faces is

Three of the faces of the tetrahedron are isosceles right triangles with legs of length 8, and, subsequently, by the 45-45-90 Theorem, hypotenuses of length 

Each of the three right triangle faces has area equal to half the product of its legs , which is

The equilateral face has as its area
The sum of the areas of the faces is
← Didn't Know|Knew It →

The cube in the above figure has surface area 384. Give the surface area of the tetrahedron with vertices  , shown in red.
, shown in red.

The cube in the above figure has surface area 384. Give the surface area of the tetrahedron with vertices 
Tap to reveal answer
The surface area formula can be used to find the length of each edge of the cube:


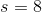
Three faces of the tetrahedron -  ,
, 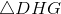 ,
,  - are right triangles with legs of length 8, so the area of each is half the product of the lengths of their legs:
- are right triangles with legs of length 8, so the area of each is half the product of the lengths of their legs:
 .
.
Each triangle is isosceles, so, by the 45-45-90 Theorem, each of their hypotentuses measures  times a leg, or
times a leg, or  . is therefore an equilateral triangle with sidelenghth
. is therefore an equilateral triangle with sidelenghth  . Its area can be found as follows:
. Its area can be found as follows:


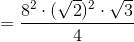

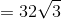
The total surface area is

The surface area formula can be used to find the length of each edge of the cube:
Three faces of the tetrahedron - 
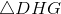


Each triangle is isosceles, so, by the 45-45-90 Theorem, each of their hypotentuses measures 


The total surface area is
← Didn't Know|Knew It →

The above diagram shows a regular right triangular pyramid. Its base  is an equilateral triangle; the other three faces are congruent isosceles triangles, with
is an equilateral triangle; the other three faces are congruent isosceles triangles, with  an altitude of
an altitude of  . Give the surface area of the pyramid.
. Give the surface area of the pyramid.

The above diagram shows a regular right triangular pyramid. Its base 


Tap to reveal answer
The base is an equilateral triangle with sidelength 12, so its area can be calculated as follows:
 .
.
Each of the three other faces is congruent, with base 12. The area of each is the product of its base and its height. To find the common height, we examine  , which, since
, which, since  is an altitude of isosceles
is an altitude of isosceles  , is a right triangle with hypotenuse of length 18 and one leg of length
, is a right triangle with hypotenuse of length 18 and one leg of length  . We can find
. We can find  using the Pythagorean Theorem:
using the Pythagorean Theorem:





The area of  is half the product of this height and the base:
is half the product of this height and the base:

All three lateral faces have this area.
Now add the areas of the four faces:

The base is an equilateral triangle with sidelength 12, so its area can be calculated as follows:

Each of the three other faces is congruent, with base 12. The area of each is the product of its base and its height. To find the common height, we examine 




The area of 
All three lateral faces have this area.
Now add the areas of the four faces:
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
What is the volume of a cube whose diagonal measures 10 inches?
What is the volume of a cube whose diagonal measures 10 inches?
Tap to reveal answer
By an extension of the Pythagorean Theorem, if  is the length of an edge of the cube and
is the length of an edge of the cube and  is its diagonal length,
is its diagonal length,




The volume  is therefore
is therefore

By an extension of the Pythagorean Theorem, if 

The volume 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A cube of iron has a mass of 4 kg. What is the mass of a rectangular prism of iron that is the same height but has a width and length that are twice as long as the cube?
A cube of iron has a mass of 4 kg. What is the mass of a rectangular prism of iron that is the same height but has a width and length that are twice as long as the cube?
Tap to reveal answer
Let the length of the sides of the cube equal 1. The volume of the cube is then 1times 1times 1=1. Therefore, the volume of the prism is 2times 2times 1=4. Therefore, the mass of the prism must be 4 times greater than the mass of the cube.
(4)(4)= 16
Let the length of the sides of the cube equal 1. The volume of the cube is then 1times 1times 1=1. Therefore, the volume of the prism is 2times 2times 1=4. Therefore, the mass of the prism must be 4 times greater than the mass of the cube.
(4)(4)= 16
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The sum of the length, the width, and the height of a rectangular prism is one yard. The length of the prism is eleven inches greater than its width, and the width is twice its height. What is the volume of the prism?
The sum of the length, the width, and the height of a rectangular prism is one yard. The length of the prism is eleven inches greater than its width, and the width is twice its height. What is the volume of the prism?
Tap to reveal answer
Let  be the height of the prism. Then the width is
be the height of the prism. Then the width is  , and the length is
, and the length is  . Since the sum of the three dimensions is one yard, or 36 inches, we solve for
. Since the sum of the three dimensions is one yard, or 36 inches, we solve for  in this equation:
in this equation:






The height is 5 inches; the width is twice this, or 10 inches; the length is eleven inches greater than the width, or 21 inches. The volume is the product of the three dimensions:
 cubic inches.
cubic inches.
Let 



The height is 5 inches; the width is twice this, or 10 inches; the length is eleven inches greater than the width, or 21 inches. The volume is the product of the three dimensions:

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
The length, width, and height of a rectangular prism, in inches, are three different prime numbers. All three dimensions are between one yard and four feet. What is the volume of the prism?
The length, width, and height of a rectangular prism, in inches, are three different prime numbers. All three dimensions are between one yard and four feet. What is the volume of the prism?
Tap to reveal answer
One yard is equal to 36 inches; four feet are equal to 48 inches. There are four prime numbers between 36 and 48 - 37, 41, 43, and 47. Since we are only given that the dimensions are three different prime numbers between 36 and 48, we have no way of knowing which three they are.
One yard is equal to 36 inches; four feet are equal to 48 inches. There are four prime numbers between 36 and 48 - 37, 41, 43, and 47. Since we are only given that the dimensions are three different prime numbers between 36 and 48, we have no way of knowing which three they are.
← Didn't Know|Knew It →