ISEE Upper Level (grades 9-12) Quantitative Reasoning
Help Questions
ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Reasoning › ISEE Upper Level (grades 9-12) Quantitative Reasoning

In the above figure, 

Which is the greater quantity?
(a) Three times the area of Trapezoid
(b) Twice the area of Trapezoid
(b) is the greater quantity
(a) is the greater quantity
(a) and (b) are equal
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
Explanation
Midsegment 


The area of a trapezoid is one half multiplied by its height multiplied by the sum of the lengths of its bases. Therefore, the area of Trapezoid 

Three times this is

The area of Trapezoid 
Twice this is

That makes (b) the greater quantity.
A pair of fair dice are rolled. Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The probability that at least one die comes up 5 or 6
(b)
(a) is greater
(b) is greater
(a) and (b) are equal
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
Explanation
For the roll to be unfavorable to the event that at least one of the dice is 5 or 6, both dice would have to be 1, 2, 3, or 4. There are 



The above diagram depicts trapezoid 
(a)
(b)
(a) and (b) are equal.
(a) is greater.
(b) is greater.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
Explanation





The Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem states that if two parallel lines are crossed by a transversal, then the sum of the measures of a pair of same-side interior angles is always 
Therefore, 
One side of a regular pentagon is 20% longer than one side of a regular hexagon. Which is the greater quantity?
(A) The perimeter of the pentagon
(B) The perimeter of the hexagon
(A) and (B) are equal
(B) is greater
(A) is greater
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
Explanation
Let 

Each side of the pentagon is 20% greater than this length, or

The perimeter is five times this, or 
The perimeters are the same.

Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale
The above figure shows Rhombus 
Which is the greater quantity?
(a)
(b)
(a) and (b) are equal
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(b) is the greater quantity
(a) is the greater quantity
Explanation
The opposite sides of a parallelogram - a rhombus included - are congruent, so

Also, Quadrilateral 


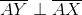



In the above figure, 


Explanation
Midsegment 


The area of a trapezoid is one half multiplied by its height multiplied by the sum of the lengths of its bases. Therefore, the area of Trapezoid 
The area of Trapezoid 
The percent of Trapezoid 
A rectangle is two feet shorter than twice its width; its perimeter is six yards. Give its area in square inches.
Explanation
The length of the rectangle is two feet, or 24 inches, shorter than twice the width, so, if 
Six yards, the perimeter of the rectangle, is equal to 

The length and width are 64 inches and 44 inches; the area is their product, which is

Given Trapezoid 

Which is the greater quantity?
(a)
(b)
(a) is greater
(b) is greater
(a) and (b) are equal
It is impossible to tell from the information given
Explanation




The Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem states that if two parallel lines are crossed by a transversal, then the sum of the measures of a pair of same-side interior angles is always 


Substitute:
(a) is the greater quantity
A pair of fair dice are tossed. Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The probability that the sum will be at least eight
(b) The probability that the sum will be at most six
(a) and (b) are equal
(a) is greater
(b) is greater
It is impossible to tell from the information given
Explanation
The following table illustrates the ways that the dice can come up. The orange cells indicate a roll of 6 or less; the pink cells indicate a roll of eight or more.

Since each of these outcomes are equally likely, and there are fifteen outcomes that are favorable to each of the two events, the probabilities are the same.
The expression is undefined.
Explanation
The numerator is undefined, since 0 raised to the power of 0 is an undefined quantity. Therefore, the entire expression is undefined.


















































