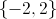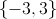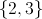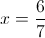Solving Non Quadratic Polynomials
Help Questions
Math › Solving Non Quadratic Polynomials
If 



Explanation
To find 

We can now use this value to find 
Our final answer is therefore
Factor 
Explanation
First, we can factor a 
Now we can make a clever substitution. If we make 
This makes it much easier to see how we can factor (difference of squares):
The last thing we need to do is substitute 


Substituting back in gives us a result of:
Give all real solutions of the following equation:
Explanation
By substituting 

We are looking to factor the quadratic expression as 


Substitute back:
The first factor cannot be factored further. The second factor, however, can itself be factored as the difference of squares:
Set each factor to zero and solve:
Since no real number squared is equal to a negative number, no real solution presents itself here.
The solution set is 
Consider the equation 
According to the Rational Zeroes Theorem, if 
Explanation
By the Rational Zeroes Theorem, any rational solution must be a factor of the constant, 6, divided by the factor of the leading coefficient, 14.
Four of the answer choices have this characteristic:

Factor:
Explanation
Using the difference of cubes formula:
Find x and y:
Plug into the formula:
Which Gives:
And cannot be factored more so the above is your final answer.
Simplify:
Explanation
Use the difference of squares to factor out the numerator.
The term 

Replace the fraction.
Simplify the top and bottom.
The answer is:
Factor by grouping.
Explanation
The first step is to determine if all of the terms have a greatest common factor (GCF). Since a GCF does not exist, we can move onto the next step.
Create smaller groups within the expression. This is typically done by grouping the first two terms and the last two terms.
Factor out the GCF from each group:
At this point, you can see that the terms inside the parentheses are identical, which means you are on the right track!
Since there is a GCF of (5x+1), we can rewrite the expression like this:
And that is your answer! You can always check your factoring by FOILing your answer and checking it against the original expression.
Factor completely:
The polynomial is prime.
Explanation
This can be most easily solved by setting 



The quadratic factors do not fit any factoring pattern and are prime, so this is as far as the polynomial can be factored.
Which of the following displays the full real-number solution set for 
Explanation
Rewriting the equation as