Circulatory and Respiratory Systems - NCLEX-PN
Card 0 of 640
What is the average amount of blood in the adult body?
What is the average amount of blood in the adult body?
Tap to see back →
The average adult body contains 4.5-6 liters of blood, depending on size and gender. Blood volume (BV) can be calculated by the following formula, given the hematocrit (HC) and plasma volume (PV):

The average adult body contains 4.5-6 liters of blood, depending on size and gender. Blood volume (BV) can be calculated by the following formula, given the hematocrit (HC) and plasma volume (PV):
The most common free plasma proteins include all of the following except .
The most common free plasma proteins include all of the following except .
Tap to see back →
The three main types of proteins in the blood are albumin, globulin, and fibrinogen. Major histocompatibility complex is not a free plasma protein, but rather a class of proteins found on the surface of all nucleated cells (MHC class I) and on the surface of certain immune cells known as antigen-presenting cells (MHC class II). They play an important part in immune function by displaying foreign antigens for communication between leukocytes.
The three main types of proteins in the blood are albumin, globulin, and fibrinogen. Major histocompatibility complex is not a free plasma protein, but rather a class of proteins found on the surface of all nucleated cells (MHC class I) and on the surface of certain immune cells known as antigen-presenting cells (MHC class II). They play an important part in immune function by displaying foreign antigens for communication between leukocytes.
Which of the following blood cells is anucleate (lacking a nucleus)?
Which of the following blood cells is anucleate (lacking a nucleus)?
Tap to see back →
The only anucleate blood cells are erythrocytes, or red blood cells. These cells are created with nuclei, but each daughter cell will then lose its nucleus in order to create more suface area for hemoglobin to bind oxygen and for easier passage through narrow capillaries.
The only anucleate blood cells are erythrocytes, or red blood cells. These cells are created with nuclei, but each daughter cell will then lose its nucleus in order to create more suface area for hemoglobin to bind oxygen and for easier passage through narrow capillaries.
How does parasympathetic innervation affect the heart?
How does parasympathetic innervation affect the heart?
Tap to see back →
Sympathetic innervation will decrease the heart rate, which will automatically decrease the cardiac output 
Sympathetic innervation will decrease the heart rate, which will automatically decrease the cardiac output
Parasympathetic innervation of the heart is primarily controlled by what nerve?
Parasympathetic innervation of the heart is primarily controlled by what nerve?
Tap to see back →
The vagus nerve provides the main parasympathetic innervation of the heart. The recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve, innervates the majority of the intrinsic muscles of the larynx. The cardiac nerve is part of the sympathetic innervation of the heart.
The vagus nerve provides the main parasympathetic innervation of the heart. The recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve, innervates the majority of the intrinsic muscles of the larynx. The cardiac nerve is part of the sympathetic innervation of the heart.
What coronary artery supplies left atrium and left ventricle?
What coronary artery supplies left atrium and left ventricle?
Tap to see back →
The majority of blood supply to the left atrium and left ventricle is provided by the left coronary artery. The septal branches and left circumflex artery are smaller divisions of this main artery. The posterior descending artery supplies the posterior one-third of the interventricular septum.
The majority of blood supply to the left atrium and left ventricle is provided by the left coronary artery. The septal branches and left circumflex artery are smaller divisions of this main artery. The posterior descending artery supplies the posterior one-third of the interventricular septum.
A nurse is performing an abdominal exam and notices a strong pulse in the abdomen just above the umbilicus. She is most likely palpating what blood vessel?
A nurse is performing an abdominal exam and notices a strong pulse in the abdomen just above the umbilicus. She is most likely palpating what blood vessel?
Tap to see back →
The nurse is most likely palpating the abdominal aorta. This vessel is large, generally 2.5-4 cm in diameter, and a strong pulse can often be felt on palpation. The femoral artery is also an area where a pulse may be felt, but it is only palpable in the mid-inguinal point of the inner thigh. The exterior iliac artery branches off of the abdominal aorta below the umbilicus, and the inferior mesenteric artery is a minor artery and is not generally palpable on examination.
The nurse is most likely palpating the abdominal aorta. This vessel is large, generally 2.5-4 cm in diameter, and a strong pulse can often be felt on palpation. The femoral artery is also an area where a pulse may be felt, but it is only palpable in the mid-inguinal point of the inner thigh. The exterior iliac artery branches off of the abdominal aorta below the umbilicus, and the inferior mesenteric artery is a minor artery and is not generally palpable on examination.
Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic system?
Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic system?
Tap to see back →
The lymphatic system has several roles in the body, including drainage of interstitial fluid from tissues, transportation and activation of lymphocytes, and absorption and transportation of dietary fats. Red blood cells, however, are unable to enter lymph vessels, and so the lymphatic system does not participate in any type of gas exchange.
The lymphatic system has several roles in the body, including drainage of interstitial fluid from tissues, transportation and activation of lymphocytes, and absorption and transportation of dietary fats. Red blood cells, however, are unable to enter lymph vessels, and so the lymphatic system does not participate in any type of gas exchange.
What organ of the lymphatic system is the site of T-cell maturation?
What organ of the lymphatic system is the site of T-cell maturation?
Tap to see back →
T-cell maturation occurs in the thymus, a small organ located in the upper part of the mediastinum, between the heart and the sternum. Mature T cells then may either circulate in the lymph or blood or reside in lymph nodes. The spleen is not a site of T cell maturation, though it does have other important immune functions, such as the production of antibodies and the removal of antibody-coated pathogens. The cisterna chyli is a part of the lymphatic system that is involved in lipid digestion.
T-cell maturation occurs in the thymus, a small organ located in the upper part of the mediastinum, between the heart and the sternum. Mature T cells then may either circulate in the lymph or blood or reside in lymph nodes. The spleen is not a site of T cell maturation, though it does have other important immune functions, such as the production of antibodies and the removal of antibody-coated pathogens. The cisterna chyli is a part of the lymphatic system that is involved in lipid digestion.
Digestive fat is absorbed through what specialized lymphatic vessels of the small intestine?
Digestive fat is absorbed through what specialized lymphatic vessels of the small intestine?
Tap to see back →
Dietary fat is absorbed via lacteals, small lymph vessels contained within the body of the intestinal villi. Microvilli, tiny projections covering the surface of the villi, help with the absorption of minerals, vitamins, and other micronutrients. The cisterna chyli is a dilated pouch at the lower end of the thoracic duct that serves as a collection point for fatty chyle from the intestinal lacteals.
Dietary fat is absorbed via lacteals, small lymph vessels contained within the body of the intestinal villi. Microvilli, tiny projections covering the surface of the villi, help with the absorption of minerals, vitamins, and other micronutrients. The cisterna chyli is a dilated pouch at the lower end of the thoracic duct that serves as a collection point for fatty chyle from the intestinal lacteals.
Which of the following is the proper unit of measurement for blood pressure?
Which of the following is the proper unit of measurement for blood pressure?
Tap to see back →
The proper unit when recording a patient's blood pressure is mmHg, or millimeter of mercury. This is derived from a historical measurement of how many millimeters of mercury in a mercury manometer were able to be elevated by a particular pressure. Due to it's toxicity, are longer used in medical equipment, though the 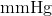 unit remains in use.
unit remains in use.
The proper unit when recording a patient's blood pressure is mmHg, or millimeter of mercury. This is derived from a historical measurement of how many millimeters of mercury in a mercury manometer were able to be elevated by a particular pressure. Due to it's toxicity, are longer used in medical equipment, though the 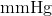
A patient has a 49 year history of hypertension. Which part of the heart would be most enlarged on echocardiogram?
A patient has a 49 year history of hypertension. Which part of the heart would be most enlarged on echocardiogram?
Tap to see back →
The left ventricle is the most commonly enlarged heart structure seen in chronic hypertension. The left ventricle must overcome the afterload of the arterial system by becoming hypertrophied. As a result, the heart gets remodeled to overcome the systemic high blood pressures. The left ventricle directly pumps blood from the heart to the systemic circuit.
The left ventricle is the most commonly enlarged heart structure seen in chronic hypertension. The left ventricle must overcome the afterload of the arterial system by becoming hypertrophied. As a result, the heart gets remodeled to overcome the systemic high blood pressures. The left ventricle directly pumps blood from the heart to the systemic circuit.
What does the term "partial pressure" describe?
What does the term "partial pressure" describe?
Tap to see back →
Many gases, such as room air, are composed of several gasses (in the case of room air, primarily nitrogen, oxygen, and several trace gasses). Partial pressure is the amount of pressure that each gas contributes. To find the total pressure of a gas mixture, one would find the sum of all partial pressures of each individual gas.
Many gases, such as room air, are composed of several gasses (in the case of room air, primarily nitrogen, oxygen, and several trace gasses). Partial pressure is the amount of pressure that each gas contributes. To find the total pressure of a gas mixture, one would find the sum of all partial pressures of each individual gas.
Which of the following structures is the site of gas exchange in the lung?
Which of the following structures is the site of gas exchange in the lung?
Tap to see back →
Gas exchange in the lung occurs exclusively in the alveoli, the tiny grape-like clusters of sacks at the terminus of the bronchioles of the lung. The gas contained in the larger structures of the lung - the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, is termed "dead space" as it does not participate in gas exchange.
Gas exchange in the lung occurs exclusively in the alveoli, the tiny grape-like clusters of sacks at the terminus of the bronchioles of the lung. The gas contained in the larger structures of the lung - the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, is termed "dead space" as it does not participate in gas exchange.
How do oxygen and carbon dioxide cross the capillary epithelium and alveolar cell membranes during gas exchange?
How do oxygen and carbon dioxide cross the capillary epithelium and alveolar cell membranes during gas exchange?
Tap to see back →
Gas exchange in the alveoli occurs by the process of simple diffusion. The blood that enters the lung capillaries is relatively low in oxygen and high in  , in comparison to the room air that is drawn into the alveoli during respiration. The separation between the capillaries and the alveolar epithelium is thin enough that these gasses can exchange across their pressure gradients by the process of simple diffusion.
, in comparison to the room air that is drawn into the alveoli during respiration. The separation between the capillaries and the alveolar epithelium is thin enough that these gasses can exchange across their pressure gradients by the process of simple diffusion.
Gas exchange in the alveoli occurs by the process of simple diffusion. The blood that enters the lung capillaries is relatively low in oxygen and high in 
Which of the following is the main trigger for the impulse to breathe?
Which of the following is the main trigger for the impulse to breathe?
Tap to see back →
The main trigger for the impulse to breathe is high carbon dioxide (decreased blood pH). In response to a decrease in blood pH, the medullary respiratory center triggers the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles to increase breathing rate.
The main trigger for the impulse to breathe is high carbon dioxide (decreased blood pH). In response to a decrease in blood pH, the medullary respiratory center triggers the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles to increase breathing rate.
Myoglobin can bind with molecule(s) of oxygen, while hemoglobin can bind with molecule(s) of oxygen.
Myoglobin can bind with molecule(s) of oxygen, while hemoglobin can bind with molecule(s) of oxygen.
Tap to see back →
Myoglobin, an oxygen-binding protein in the muscle tissue, can bind with one molecule of oxygen. Hemoglobin, the main oxygen-binding metalloprotein in red blood cells, can bind four molecules of oxygen.
Myoglobin, an oxygen-binding protein in the muscle tissue, can bind with one molecule of oxygen. Hemoglobin, the main oxygen-binding metalloprotein in red blood cells, can bind four molecules of oxygen.
Hyperventilation results in which of the following?
Hyperventilation results in which of the following?
Tap to see back →
While hyperventilation or tachypnea may be triggered by various forms of acidosis, they will not cause a decrease in blood pH, but rather push the blood into a more alkaline state. This occurs due to loss of carbon dioxide during respiration, followed by a compensatory decrease in bicarbonate ions. The result is in an elevation in the pH of the blood. This condition is known as respiratory alkalosis.
While hyperventilation or tachypnea may be triggered by various forms of acidosis, they will not cause a decrease in blood pH, but rather push the blood into a more alkaline state. This occurs due to loss of carbon dioxide during respiration, followed by a compensatory decrease in bicarbonate ions. The result is in an elevation in the pH of the blood. This condition is known as respiratory alkalosis.
How many lobes total are there in the human lungs?
How many lobes total are there in the human lungs?
Tap to see back →
There are five lobes total in the human lungs: the right lung has three lobes (the upper lobe, the middle lobe, and the lower lobe) while the left lung has two lobes (the upper lobe and the lower lobe).
There are five lobes total in the human lungs: the right lung has three lobes (the upper lobe, the middle lobe, and the lower lobe) while the left lung has two lobes (the upper lobe and the lower lobe).
What is the name for the topmost part of the lung?
What is the name for the topmost part of the lung?
Tap to see back →
The topmost part of the lungs is the apex. This area extends into the neck above the 1st rib and is the location auscultated for a diagnosis of a pancost tumor. The lingula of the lung is a small flap of the lowest part of the upper lobe of the left lung. The hilum is the entry point of the lung for the bronchi, pulmonary artery and vein, and nerves. The trachea is not a part of the lung at all; it is the cartilaginous tube that connects the pharynx and larynx to the lung.
The topmost part of the lungs is the apex. This area extends into the neck above the 1st rib and is the location auscultated for a diagnosis of a pancost tumor. The lingula of the lung is a small flap of the lowest part of the upper lobe of the left lung. The hilum is the entry point of the lung for the bronchi, pulmonary artery and vein, and nerves. The trachea is not a part of the lung at all; it is the cartilaginous tube that connects the pharynx and larynx to the lung.