Using Dichromate Compounds - Organic Chemistry
Card 1 of 16
A chemist adds the orange oxidizing agent, Na2Cr2O7, to the following substrates and dissolves the mixture in an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid. Oxidation is indicated by the disappearance of the orange color. Which of the substrate-oxidant solutions will remain orange?
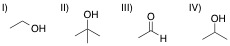
A chemist adds the orange oxidizing agent, Na2Cr2O7, to the following substrates and dissolves the mixture in an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid. Oxidation is indicated by the disappearance of the orange color. Which of the substrate-oxidant solutions will remain orange?
Tap to reveal answer
The following reaction schemes show the oxidation of all substrates, indicating that substrate II is in the highest oxidation state possible, and that an oxidation of this compound will not proceed.
Remember that in sulfuric acid and water, Na2Cr2O7 will be converted to CrO3, the active oxidant species. Furthermore, the oxidation mechanism involving this species includes the key step in which a hydrogen bonded to the carbon in question is eliminated_,_ and simutaneously, a double bond from that carbon to an oxygen is installed. Thus, all substrates that feature at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbon to be oxidized can and will be oxidized in the precense of chromium trioxide.
Lastly, remember that these reactions are taking place in the prescence of water. While substrates such as compound III do not appear to be oxidizable, attack of water at the aldehyde carbon will give a dialcohol tetrathedral intermediate that can be immediately oxidized by chromium trioxide to the corresponding carboxylic acid. A similar mechanism occurs for substrate I, wherein, after the ketone oxidation state is achieved, an attack of water furnishes the same dialcohol intermediate that is oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Remember that the highest oxidation state available for organic compounds containing more than one carbon is the carboxylic acid oxidation state. Chromium trioxide will oxidize all organics to this oxidation state, unless directly-bonded hydrogens are not present in lower oxidation states, such as shown with substrate IV.

The following reaction schemes show the oxidation of all substrates, indicating that substrate II is in the highest oxidation state possible, and that an oxidation of this compound will not proceed.
Remember that in sulfuric acid and water, Na2Cr2O7 will be converted to CrO3, the active oxidant species. Furthermore, the oxidation mechanism involving this species includes the key step in which a hydrogen bonded to the carbon in question is eliminated_,_ and simutaneously, a double bond from that carbon to an oxygen is installed. Thus, all substrates that feature at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbon to be oxidized can and will be oxidized in the precense of chromium trioxide.
Lastly, remember that these reactions are taking place in the prescence of water. While substrates such as compound III do not appear to be oxidizable, attack of water at the aldehyde carbon will give a dialcohol tetrathedral intermediate that can be immediately oxidized by chromium trioxide to the corresponding carboxylic acid. A similar mechanism occurs for substrate I, wherein, after the ketone oxidation state is achieved, an attack of water furnishes the same dialcohol intermediate that is oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Remember that the highest oxidation state available for organic compounds containing more than one carbon is the carboxylic acid oxidation state. Chromium trioxide will oxidize all organics to this oxidation state, unless directly-bonded hydrogens are not present in lower oxidation states, such as shown with substrate IV.

← Didn't Know|Knew It →

Which of the following reagents would satisfy the given reaction?
Which of the following reagents would satisfy the given reaction?
Tap to reveal answer
In order to drive the reactant, we must first convert the alcohol group on the ethanol into a carboxylic acid. We do so by using the oxidizing agent,  , a very strong oxidizing agent that is well known to oxidize primary alcohols into carboxylic acids (among other functions). Once we have our carboxylic acid, we can simply use
, a very strong oxidizing agent that is well known to oxidize primary alcohols into carboxylic acids (among other functions). Once we have our carboxylic acid, we can simply use  to convert our carboxylic acid into an acid halide to attain our desired final product.
to convert our carboxylic acid into an acid halide to attain our desired final product.
In order to drive the reactant, we must first convert the alcohol group on the ethanol into a carboxylic acid. We do so by using the oxidizing agent, 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following substrates will be oxidized into a ketone when reacting with 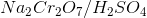 ?
?
Which of the following substrates will be oxidized into a ketone when reacting with 
Tap to reveal answer
 is a strong oxidizing agent.
is a strong oxidizing agent.
Not only can  reduce secondary alcohols into ketones, but it can reduce primary alcohols and aldehydes into carboxylic acids.
reduce secondary alcohols into ketones, but it can reduce primary alcohols and aldehydes into carboxylic acids.

Not only can 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →

What would be the product of the given reaction?

What would be the product of the given reaction?
Tap to reveal answer
The reaction given would give a ketone. This type of reaction is called an oxidation reaction. Oxidation of a secondary alcohol as in the reaction given by  (sodium dichromate) in an aqueous solution of
(sodium dichromate) in an aqueous solution of  (acetic acid) solvent yields a ketone. However, if we performed the same reaction with a primary alcohol, a carboxylic acid would have formed.
(acetic acid) solvent yields a ketone. However, if we performed the same reaction with a primary alcohol, a carboxylic acid would have formed.
The reaction given would give a ketone. This type of reaction is called an oxidation reaction. Oxidation of a secondary alcohol as in the reaction given by 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →

Which of the following reagents would satisfy the given reaction?
Which of the following reagents would satisfy the given reaction?
Tap to reveal answer
In order to drive the reactant, we must first convert the alcohol group on the ethanol into a carboxylic acid. We do so by using the oxidizing agent,  , a very strong oxidizing agent that is well known to oxidize primary alcohols into carboxylic acids (among other functions). Once we have our carboxylic acid, we can simply use
, a very strong oxidizing agent that is well known to oxidize primary alcohols into carboxylic acids (among other functions). Once we have our carboxylic acid, we can simply use  to convert our carboxylic acid into an acid halide to attain our desired final product.
to convert our carboxylic acid into an acid halide to attain our desired final product.
In order to drive the reactant, we must first convert the alcohol group on the ethanol into a carboxylic acid. We do so by using the oxidizing agent, 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following substrates will be oxidized into a ketone when reacting with 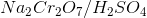 ?
?
Which of the following substrates will be oxidized into a ketone when reacting with 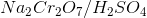
Tap to reveal answer
 is a strong oxidizing agent.
is a strong oxidizing agent.
Not only can  reduce secondary alcohols into ketones, but it can reduce primary alcohols and aldehydes into carboxylic acids.
reduce secondary alcohols into ketones, but it can reduce primary alcohols and aldehydes into carboxylic acids.

Not only can 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A chemist adds the orange oxidizing agent, Na2Cr2O7, to the following substrates and dissolves the mixture in an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid. Oxidation is indicated by the disappearance of the orange color. Which of the substrate-oxidant solutions will remain orange?
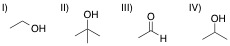
A chemist adds the orange oxidizing agent, Na2Cr2O7, to the following substrates and dissolves the mixture in an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid. Oxidation is indicated by the disappearance of the orange color. Which of the substrate-oxidant solutions will remain orange?
Tap to reveal answer
The following reaction schemes show the oxidation of all substrates, indicating that substrate II is in the highest oxidation state possible, and that an oxidation of this compound will not proceed.
Remember that in sulfuric acid and water, Na2Cr2O7 will be converted to CrO3, the active oxidant species. Furthermore, the oxidation mechanism involving this species includes the key step in which a hydrogen bonded to the carbon in question is eliminated_,_ and simutaneously, a double bond from that carbon to an oxygen is installed. Thus, all substrates that feature at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbon to be oxidized can and will be oxidized in the precense of chromium trioxide.
Lastly, remember that these reactions are taking place in the prescence of water. While substrates such as compound III do not appear to be oxidizable, attack of water at the aldehyde carbon will give a dialcohol tetrathedral intermediate that can be immediately oxidized by chromium trioxide to the corresponding carboxylic acid. A similar mechanism occurs for substrate I, wherein, after the ketone oxidation state is achieved, an attack of water furnishes the same dialcohol intermediate that is oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Remember that the highest oxidation state available for organic compounds containing more than one carbon is the carboxylic acid oxidation state. Chromium trioxide will oxidize all organics to this oxidation state, unless directly-bonded hydrogens are not present in lower oxidation states, such as shown with substrate IV.

The following reaction schemes show the oxidation of all substrates, indicating that substrate II is in the highest oxidation state possible, and that an oxidation of this compound will not proceed.
Remember that in sulfuric acid and water, Na2Cr2O7 will be converted to CrO3, the active oxidant species. Furthermore, the oxidation mechanism involving this species includes the key step in which a hydrogen bonded to the carbon in question is eliminated_,_ and simutaneously, a double bond from that carbon to an oxygen is installed. Thus, all substrates that feature at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbon to be oxidized can and will be oxidized in the precense of chromium trioxide.
Lastly, remember that these reactions are taking place in the prescence of water. While substrates such as compound III do not appear to be oxidizable, attack of water at the aldehyde carbon will give a dialcohol tetrathedral intermediate that can be immediately oxidized by chromium trioxide to the corresponding carboxylic acid. A similar mechanism occurs for substrate I, wherein, after the ketone oxidation state is achieved, an attack of water furnishes the same dialcohol intermediate that is oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Remember that the highest oxidation state available for organic compounds containing more than one carbon is the carboxylic acid oxidation state. Chromium trioxide will oxidize all organics to this oxidation state, unless directly-bonded hydrogens are not present in lower oxidation states, such as shown with substrate IV.

← Didn't Know|Knew It →

What would be the product of the given reaction?

What would be the product of the given reaction?
Tap to reveal answer
The reaction given would give a ketone. This type of reaction is called an oxidation reaction. Oxidation of a secondary alcohol as in the reaction given by  (sodium dichromate) in an aqueous solution of
(sodium dichromate) in an aqueous solution of  (acetic acid) solvent yields a ketone. However, if we performed the same reaction with a primary alcohol, a carboxylic acid would have formed.
(acetic acid) solvent yields a ketone. However, if we performed the same reaction with a primary alcohol, a carboxylic acid would have formed.
The reaction given would give a ketone. This type of reaction is called an oxidation reaction. Oxidation of a secondary alcohol as in the reaction given by 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →

Which of the following reagents would satisfy the given reaction?
Which of the following reagents would satisfy the given reaction?
Tap to reveal answer
In order to drive the reactant, we must first convert the alcohol group on the ethanol into a carboxylic acid. We do so by using the oxidizing agent,  , a very strong oxidizing agent that is well known to oxidize primary alcohols into carboxylic acids (among other functions). Once we have our carboxylic acid, we can simply use
, a very strong oxidizing agent that is well known to oxidize primary alcohols into carboxylic acids (among other functions). Once we have our carboxylic acid, we can simply use  to convert our carboxylic acid into an acid halide to attain our desired final product.
to convert our carboxylic acid into an acid halide to attain our desired final product.
In order to drive the reactant, we must first convert the alcohol group on the ethanol into a carboxylic acid. We do so by using the oxidizing agent, 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following substrates will be oxidized into a ketone when reacting with 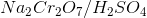 ?
?
Which of the following substrates will be oxidized into a ketone when reacting with 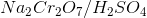
Tap to reveal answer
 is a strong oxidizing agent.
is a strong oxidizing agent.
Not only can  reduce secondary alcohols into ketones, but it can reduce primary alcohols and aldehydes into carboxylic acids.
reduce secondary alcohols into ketones, but it can reduce primary alcohols and aldehydes into carboxylic acids.

Not only can 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A chemist adds the orange oxidizing agent, Na2Cr2O7, to the following substrates and dissolves the mixture in an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid. Oxidation is indicated by the disappearance of the orange color. Which of the substrate-oxidant solutions will remain orange?
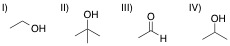
A chemist adds the orange oxidizing agent, Na2Cr2O7, to the following substrates and dissolves the mixture in an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid. Oxidation is indicated by the disappearance of the orange color. Which of the substrate-oxidant solutions will remain orange?
Tap to reveal answer
The following reaction schemes show the oxidation of all substrates, indicating that substrate II is in the highest oxidation state possible, and that an oxidation of this compound will not proceed.
Remember that in sulfuric acid and water, Na2Cr2O7 will be converted to CrO3, the active oxidant species. Furthermore, the oxidation mechanism involving this species includes the key step in which a hydrogen bonded to the carbon in question is eliminated_,_ and simutaneously, a double bond from that carbon to an oxygen is installed. Thus, all substrates that feature at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbon to be oxidized can and will be oxidized in the precense of chromium trioxide.
Lastly, remember that these reactions are taking place in the prescence of water. While substrates such as compound III do not appear to be oxidizable, attack of water at the aldehyde carbon will give a dialcohol tetrathedral intermediate that can be immediately oxidized by chromium trioxide to the corresponding carboxylic acid. A similar mechanism occurs for substrate I, wherein, after the ketone oxidation state is achieved, an attack of water furnishes the same dialcohol intermediate that is oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Remember that the highest oxidation state available for organic compounds containing more than one carbon is the carboxylic acid oxidation state. Chromium trioxide will oxidize all organics to this oxidation state, unless directly-bonded hydrogens are not present in lower oxidation states, such as shown with substrate IV.

The following reaction schemes show the oxidation of all substrates, indicating that substrate II is in the highest oxidation state possible, and that an oxidation of this compound will not proceed.
Remember that in sulfuric acid and water, Na2Cr2O7 will be converted to CrO3, the active oxidant species. Furthermore, the oxidation mechanism involving this species includes the key step in which a hydrogen bonded to the carbon in question is eliminated_,_ and simutaneously, a double bond from that carbon to an oxygen is installed. Thus, all substrates that feature at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbon to be oxidized can and will be oxidized in the precense of chromium trioxide.
Lastly, remember that these reactions are taking place in the prescence of water. While substrates such as compound III do not appear to be oxidizable, attack of water at the aldehyde carbon will give a dialcohol tetrathedral intermediate that can be immediately oxidized by chromium trioxide to the corresponding carboxylic acid. A similar mechanism occurs for substrate I, wherein, after the ketone oxidation state is achieved, an attack of water furnishes the same dialcohol intermediate that is oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Remember that the highest oxidation state available for organic compounds containing more than one carbon is the carboxylic acid oxidation state. Chromium trioxide will oxidize all organics to this oxidation state, unless directly-bonded hydrogens are not present in lower oxidation states, such as shown with substrate IV.

← Didn't Know|Knew It →

What would be the product of the given reaction?

What would be the product of the given reaction?
Tap to reveal answer
The reaction given would give a ketone. This type of reaction is called an oxidation reaction. Oxidation of a secondary alcohol as in the reaction given by  (sodium dichromate) in an aqueous solution of
(sodium dichromate) in an aqueous solution of  (acetic acid) solvent yields a ketone. However, if we performed the same reaction with a primary alcohol, a carboxylic acid would have formed.
(acetic acid) solvent yields a ketone. However, if we performed the same reaction with a primary alcohol, a carboxylic acid would have formed.
The reaction given would give a ketone. This type of reaction is called an oxidation reaction. Oxidation of a secondary alcohol as in the reaction given by 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
A chemist adds the orange oxidizing agent, Na2Cr2O7, to the following substrates and dissolves the mixture in an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid. Oxidation is indicated by the disappearance of the orange color. Which of the substrate-oxidant solutions will remain orange?
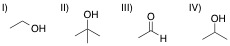
A chemist adds the orange oxidizing agent, Na2Cr2O7, to the following substrates and dissolves the mixture in an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid. Oxidation is indicated by the disappearance of the orange color. Which of the substrate-oxidant solutions will remain orange?
Tap to reveal answer
The following reaction schemes show the oxidation of all substrates, indicating that substrate II is in the highest oxidation state possible, and that an oxidation of this compound will not proceed.
Remember that in sulfuric acid and water, Na2Cr2O7 will be converted to CrO3, the active oxidant species. Furthermore, the oxidation mechanism involving this species includes the key step in which a hydrogen bonded to the carbon in question is eliminated_,_ and simutaneously, a double bond from that carbon to an oxygen is installed. Thus, all substrates that feature at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbon to be oxidized can and will be oxidized in the precense of chromium trioxide.
Lastly, remember that these reactions are taking place in the prescence of water. While substrates such as compound III do not appear to be oxidizable, attack of water at the aldehyde carbon will give a dialcohol tetrathedral intermediate that can be immediately oxidized by chromium trioxide to the corresponding carboxylic acid. A similar mechanism occurs for substrate I, wherein, after the ketone oxidation state is achieved, an attack of water furnishes the same dialcohol intermediate that is oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Remember that the highest oxidation state available for organic compounds containing more than one carbon is the carboxylic acid oxidation state. Chromium trioxide will oxidize all organics to this oxidation state, unless directly-bonded hydrogens are not present in lower oxidation states, such as shown with substrate IV.

The following reaction schemes show the oxidation of all substrates, indicating that substrate II is in the highest oxidation state possible, and that an oxidation of this compound will not proceed.
Remember that in sulfuric acid and water, Na2Cr2O7 will be converted to CrO3, the active oxidant species. Furthermore, the oxidation mechanism involving this species includes the key step in which a hydrogen bonded to the carbon in question is eliminated_,_ and simutaneously, a double bond from that carbon to an oxygen is installed. Thus, all substrates that feature at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbon to be oxidized can and will be oxidized in the precense of chromium trioxide.
Lastly, remember that these reactions are taking place in the prescence of water. While substrates such as compound III do not appear to be oxidizable, attack of water at the aldehyde carbon will give a dialcohol tetrathedral intermediate that can be immediately oxidized by chromium trioxide to the corresponding carboxylic acid. A similar mechanism occurs for substrate I, wherein, after the ketone oxidation state is achieved, an attack of water furnishes the same dialcohol intermediate that is oxidized to the carboxylic acid. Remember that the highest oxidation state available for organic compounds containing more than one carbon is the carboxylic acid oxidation state. Chromium trioxide will oxidize all organics to this oxidation state, unless directly-bonded hydrogens are not present in lower oxidation states, such as shown with substrate IV.

← Didn't Know|Knew It →

Which of the following reagents would satisfy the given reaction?
Which of the following reagents would satisfy the given reaction?
Tap to reveal answer
In order to drive the reactant, we must first convert the alcohol group on the ethanol into a carboxylic acid. We do so by using the oxidizing agent,  , a very strong oxidizing agent that is well known to oxidize primary alcohols into carboxylic acids (among other functions). Once we have our carboxylic acid, we can simply use
, a very strong oxidizing agent that is well known to oxidize primary alcohols into carboxylic acids (among other functions). Once we have our carboxylic acid, we can simply use  to convert our carboxylic acid into an acid halide to attain our desired final product.
to convert our carboxylic acid into an acid halide to attain our desired final product.
In order to drive the reactant, we must first convert the alcohol group on the ethanol into a carboxylic acid. We do so by using the oxidizing agent, 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →
Which of the following substrates will be oxidized into a ketone when reacting with 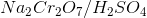 ?
?
Which of the following substrates will be oxidized into a ketone when reacting with 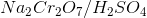
Tap to reveal answer
 is a strong oxidizing agent.
is a strong oxidizing agent.
Not only can  reduce secondary alcohols into ketones, but it can reduce primary alcohols and aldehydes into carboxylic acids.
reduce secondary alcohols into ketones, but it can reduce primary alcohols and aldehydes into carboxylic acids.

Not only can 
← Didn't Know|Knew It →

What would be the product of the given reaction?

What would be the product of the given reaction?
Tap to reveal answer
The reaction given would give a ketone. This type of reaction is called an oxidation reaction. Oxidation of a secondary alcohol as in the reaction given by  (sodium dichromate) in an aqueous solution of
(sodium dichromate) in an aqueous solution of  (acetic acid) solvent yields a ketone. However, if we performed the same reaction with a primary alcohol, a carboxylic acid would have formed.
(acetic acid) solvent yields a ketone. However, if we performed the same reaction with a primary alcohol, a carboxylic acid would have formed.
The reaction given would give a ketone. This type of reaction is called an oxidation reaction. Oxidation of a secondary alcohol as in the reaction given by 

← Didn't Know|Knew It →