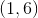All ACT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #171 : Advanced Geometry
In the standard xy coordinate plane, what quadrant(s) could point A lie in, if its x-coordinate and y-coordinate have opposite signs?
Quadrant II
Quadrant III
Quadrants IV
Quadrants I and III
Quadrants II and IV
Quadrants II and IV
We know that right of the origin represents the positive x-direction, and above the origin represents the positive y-direction. For Quadrant I, both the x-coordinate and y-coordinate must be positive, i.e. (+,+). For quadrant II, the x-coordinate is negative, while the y-coordinate is positive, i.e. (+, -). For Quadrant III, both coordinates must be negative, i.e. (-, -). For Quadrant IV, the x-coordinate is positive, and the y-coordinate is negative, i.e. (+, -).
Example Question #231 : Algebra
Which pair of coordinates lies within quadrant II?
By definition, quadrant I has positive coordinates, quadrant II has 






Example Question #232 : Algebra
In which Quadrant is the point 
Quadrant I
Quadrant IV
Quadrant III
Quadrant II
Quadrant I
To find out which quadrant a point lives in, we need to remember the qualities of each quadrant. By qualities, I mean the signs associated with the x and y values which are dependent on the quadrant the point resides in.
All coordinate pairs that are in Quadrant I will have a positive x value and a positive y value.
All coordinate pairs that are in Quadrant II will have a negative x value and a positive y value.
All coordinate pairs that are in Quadrant III will have a negative x value and a negative y value.
All coordinate pairs that are in Quadrant IV will have a positive x value and a negative y value.
For the point 
Example Question #233 : Algebra
Which of the following coordinate pairs is farthest from the origin?
Using the distance formula, calculate the distance from each of these points to the origin, (0, 0). While each answer choice has coordinates that add up to seven, (-1, 8) is the coordinate pair that produces the largest distance, namely 
Example Question #1 : How To Graph An Ordered Pair
Which point best represents the coordinate 

B
A
C
D
D
To get to 


The sign in front of each number represents which direction to go on the x or y-axis starting at the origin 
Example Question #83 : Coordinate Geometry
Which point best represents the coordinates 

D
A
B
C
A
The sign in front of each number represents which direction to go on the x or y-axis starting at the origin 
To get to 


Example Question #84 : Coordinate Geometry
Which point best represents the coordinate 

A
C
B
D
D
The sign in front of each number represents which direction to go on the x or y-axis starting at the origin 
To get to 


Example Question #3 : How To Graph An Ordered Pair
Which point best represents the coordinate 

D
B
A
C
C
To get to 


The sign in front of each number represents which direction to go on the x or y-axis starting at the origin 
Example Question #231 : Algebra
Which point best represents the coordinate 

D
C
B
A
A
To get to 


The sign in front of each number represents which direction to go on the x or y-axis starting at the origin 
Example Question #3 : How To Graph An Ordered Pair
Which point best represents the coordinate 

A
C
D
B
B
The sign in front of each number represents which direction to go on the x or y-axis starting at the origin 
To get to 


All ACT Math Resources