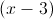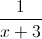All Algebra 1 Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Solution To A Binomial Problem
Solve for in terms of :
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
First, isolate X onto one side of the equation:
Next, divide both sides of the equation by 4/3:
When simplified, your answer should be:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Solution To A Binomial Problem
Solve for
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Solution To A Binomial Problem
Solve for
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Solution To A Binomial Problem
Solve for
Possible Answers:
None of the other answers.
Correct answer:
Explanation:
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Solution To A Binomial Problem
Solve for
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
Example Question #301 : Variables
Solve for
Possible Answers:
None of the other answers.
Correct answer:
Explanation:
Example Question #302 : Variables
Solve for
Possible Answers:
None of the other answers.
Correct answer:
Explanation:
Example Question #2 : Solving Rational Expressions
Simplify:
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
Factor out from the numerator which gives us
Hence we get the following
which is equal to
Example Question #1 : Factoring Rational Expressions
Simplify:
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
If we factors the denominator we get
Hence the rational expression becomes equal to
which is equal to
Example Question #303 : Variables
Which of the following fractions is NOT equivalent to ?
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
We know that is equivalent to or .
By this property, there is no way to get from .
Therefore the correct answer is .
Hellen
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
Egerton University, Kenya, Bachelor of Education, Learning Sciences. University of Applied Sciences Nuertingen, Masters in Bu...
Bryan
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
Virginia Commonwealth University, Bachelor of Science, Mathematics and Statistics.
All Algebra 1 Resources
Popular Subjects
French Tutors in Boston, Biology Tutors in New York City, SAT Tutors in Denver, Computer Science Tutors in New York City, MCAT Tutors in Seattle, ACT Tutors in San Diego, LSAT Tutors in Phoenix, ACT Tutors in Houston, Biology Tutors in Houston, SSAT Tutors in Los Angeles
Popular Courses & Classes
MCAT Courses & Classes in Boston, MCAT Courses & Classes in Atlanta, SSAT Courses & Classes in Phoenix, GRE Courses & Classes in San Diego, MCAT Courses & Classes in Chicago, GMAT Courses & Classes in Boston, GMAT Courses & Classes in Los Angeles, ACT Courses & Classes in San Francisco-Bay Area, GRE Courses & Classes in Philadelphia, Spanish Courses & Classes in Chicago
Popular Test Prep
ISEE Test Prep in Denver, MCAT Test Prep in Los Angeles, MCAT Test Prep in New York City, GRE Test Prep in Philadelphia, SAT Test Prep in Denver, GMAT Test Prep in Boston, LSAT Test Prep in New York City, MCAT Test Prep in Denver, ACT Test Prep in San Francisco-Bay Area, ISEE Test Prep in Los Angeles