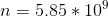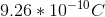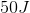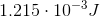All AP Physics 2 Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Circuit Components
Imagine a capacitor with a magnitude of charge Q on either plate. This capacitor has area A, separation distance D, and is connected to a battery of voltage V. If some external agent pulls the capacitor apart such that D doubles, did the charge on each plate increase, decrease or stay the same?
Increase
The charge is zero
Decrease
Stays constant
Decrease
Relevant equations:
Plug the second equation into the first:
Considering all the variables in the numerator are held fixed for this problem, we see that increasing D will decrease the charge stored on each plate.
Example Question #1 : Capacitors And Capacitance
Imagine a capacitor with a magnitude of charge Q on either plate. This capacitor has area A, separation distance D, and is not connected to a battery of voltage V. If some external agent pulls the capacitor apart such that D doubles, did the charge on each plate increase, decrease or stay the same?
Stays constant
We need to know the capacitance of the capacitor
Decrease
Increase
Stays constant
The charge has no where to go. Without the battery connected, the charge has no physical avenue on or off the plates.
Example Question #281 : Electricity And Magnetism
Imagine a capacitor with a magnitude of charge Q on either plate. This capacitor has area A, separation distance D, and is connected to a battery of voltage V. If some external agent pulls the capacitor apart such that D doubles, how did the capacitance change? Also, do we need to use the information provided about the battery?
Increase, yes
Decrease, no
Increase, no
Decrease, yes
Decrease, no
As D increases, C will decrease
Does the battery matter? No. Capacitance is a "geometric" quantity. This means that it can be determined solely by physical parameters like the area and separation distance. The charge on the plates, voltage difference, electric field and any other quantity you could think of does not influence the capacitance other than A or D.
Example Question #12 : Capacitors And Capacitance
Consider the given diagram. If 

None of these
The voltage rise through the source must be the same as the drop through the capacitor.
The voltage drop across the capacitor is the equal to the electric field multiplied by the distance.
Combine equations and find the electric field:
Convert mm to m and plugg in values:
Use the electric field in a capacitor equation:
Convert 

The magnitude of total charge on the positive plate is equal to the total charge on the negative plate, so to find the number of excess elections:
Example Question #283 : Electricity And Magnetism

Consider the given diagram. If 


The voltage rise through the source must be the same as the drop through the capacitor.
The voltage drop across the capacitor is the equal to the electric field multiplied by the distance.
Combine equations and solve for the electric field:
Convert mm to m and plug in values:
Using the electric field in a capacitor equation:
Rearrange to solve for the charge:
Convert 

Example Question #14 : Capacitors And Capacitance
Suppose I have a uniform electric field within a parallel plate capacitor with field strength of 
Suppose the capacitor's plates are 


What is the voltage difference across the capacitor?
Voltage difference 



For this problem,
Example Question #15 : Capacitors And Capacitance
Suppose I have a uniform electric field within a parallel plate capacitor with field strength of 
Suppose the capacitor's plates are 


Determine the capacitance of this system given that the space in between is a vacuum, and that the permittivity of empty space 

The formula for capacitance 

Where 



To determine 

Putting it all together,
Example Question #1 : Capacitor Energy
Consider the circuit:

If the voltage drop across C2 is 5V, what is the total energy stored in C2 and C3?
In parallel branches of a circuit, the voltage drops are all the same. Therefore, we know that the voltage drop across C3 is also 5V.
We can then use the following equation to calculate the total stored energy:
Since the voltage is the same for both capacitors, we can simply add the two capacitances to do one calculation for energy:
Example Question #121 : Circuits
A 

None of the other answers is correct
To find the amount of energy stored in a capactior, we use the equation

We're given the capacitance (

Example Question #3 : Capacitor Energy
You have 4 capacitors, 




Their capacitances are as follows:
If you have a 6V battery connected to the circuit, what's the total energy stored in the capacitors?
The equation for energy stored in a capacitor is
We can find the capacitance by adding the capacitors together, and we have the voltage, so we'll use the second equation, 
When adding capacitors, remember how to add in series and parallel.
Capacitors 





Now that we have the total capacitance, we can use the earlier equation to find the energy.
The total energy stored is 121.5J.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All AP Physics 2 Resources