All Basic Geometry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #22 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
Given the above right triangle, find the length of the missing side.
To find the length of the side x, we must use the Pythagorean Theorem

However, this time since we are given the value of the hypotenuse, we will solve for side b rather than c.
So, when we plug the given values into the formula, the equation looks like

which can be simplified to

Next, solve for b and we get a final answer of

Example Question #23 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
Find the length of the missing side of the right triangle.
To find the length of the side x, we must use the Pythagorean Theorem

However, this time since we are given the value of the hypotenuse, we will solve for side b rather than c.
So, when we plug the given values into the formula, the equation looks like

which can be simplified to

Next, solve for b and we get a final answer of

Example Question #24 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
Find the length of the missing side of the right triangle.
To find the length of the side x, we must use the Pythagorean Theorem

However, this time since we are given the value of the hypotenuse, we will solve for side b rather than c.
So, when we plug the given values into the formula, the equation looks like

which can be simplified to

Next, solve for b and we get a final answer of

Example Question #21 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
The three sides of a triangle have lengths 


True or false: the triangle is a right triangle.
True
False
False
We can rewrite each of these fractional lengths in terms of their least common denominator, which is 
By the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse, a triangle is right if and only if

where 


Therefore, we can set 
The statement is false, so the Pythagorean relationship does not hold. The triangle is not right.
Example Question #1211 : Plane Geometry
The three sides of a triangle have lengths 0.8, 1.2, and 1.5.
True or false: the triangle is a right triangle.
False
True
False
By the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse, a triangle is right if and only if

where 


Therefore, set 
The statement is false, so the Pythagorean relationship does not hold. The triangle is not right.
Example Question #32 : Right Triangles
The three sides of a triangle have lengths 


True or false: the triangle is a right triangle.
True
False
True
By the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse, a triangle is right if and only if

where 


Therefore, we can set 
The statement is true, so the Pythagorean relationship holds. The triangle is right.
Example Question #28 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle

In the right triangle shown here, 


Given the lengths of two sides of a right triangle, it is always possible to calculate the length of the third side using the Pythagorean Theorem:
Here, the given side lengths are 



Hence, the length of the base 

Example Question #29 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
Given: 



Which is a true statement?







Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A Right Triangle : Pythagorean Theorem
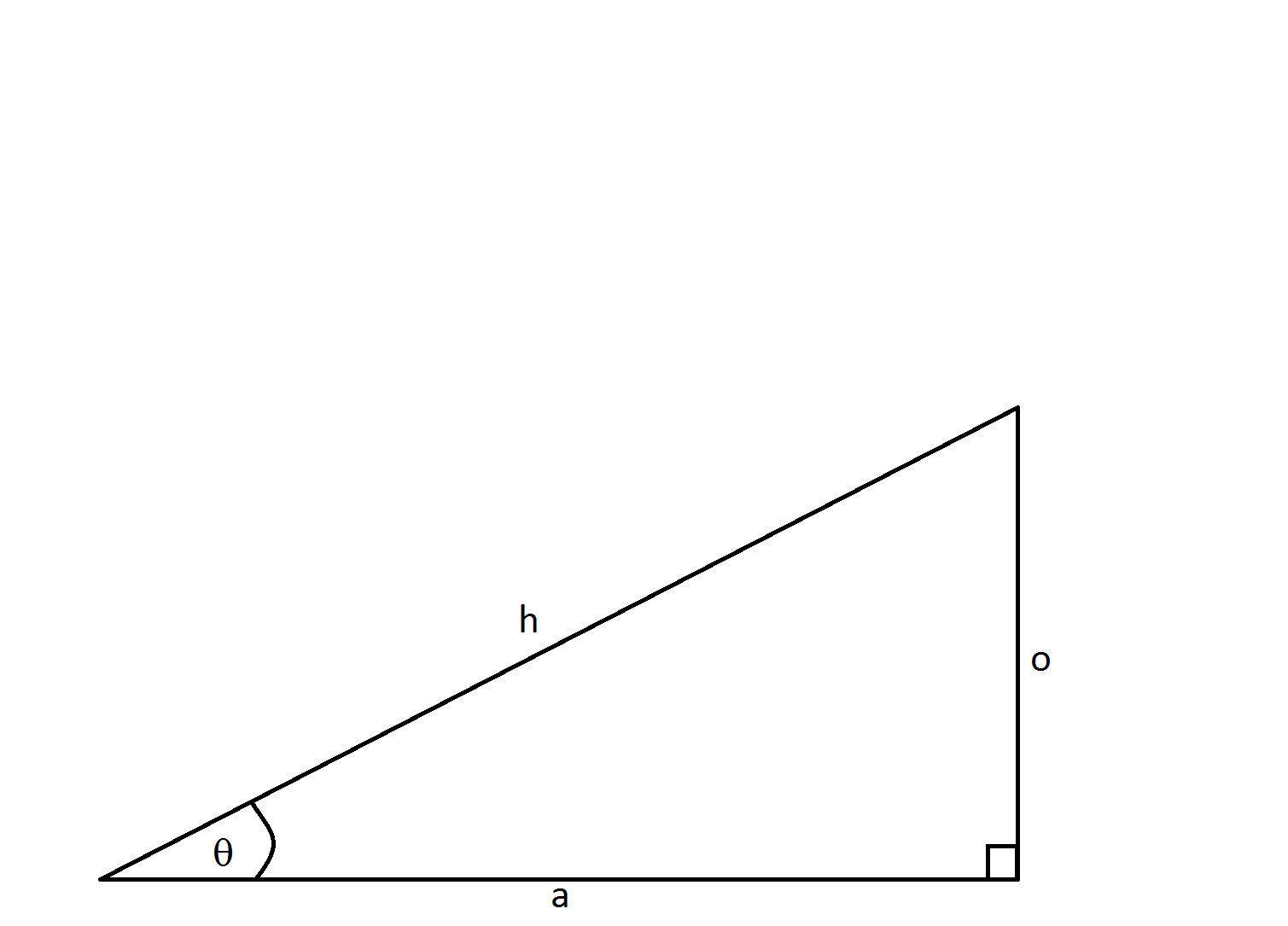
If 


Not enough information to solve
This problem is solved using the Pythagorean theorem 



Using the labels of our triangle we have:
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A Right Triangle : Pythagorean Theorem
If one of the short sides of a 45-45-90 triangle equals 5, how long is the hypotenuse?
5√2
√10
π
5
√15
5√2
Using the Pythagorean theorem, x2 + y2 = h2. And since it is a 45-45-90 triangle the two short sides are equal. Therefore 52 + 52 = h2 . Multiplied out 25 + 25 = h2.
Therefore h2 = 50, so h = √50 = √2 * √25 or 5√2.
All Basic Geometry Resources

























































