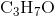All College Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #81 : Reactions
Identify the Bronsted-Lowry acid in the following equation:
Recall that a Bronsted-Lowry acid donates a proton. From the equation, we can see that 


Example Question #2 : Lewis, Brønsted Lowry, And Arrhenius Definitions
Identify the Lewis Base in the following reaction:
Recall that a Lewis base accepts a proton, while a Lewis acid donates a proton. Looking at the equation, we can see that 


Example Question #3 : Lewis, Brønsted Lowry, And Arrhenius Definitions
Which type of acid is defined by its ability to produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solution?
Lewis acid
Bronsted-Lowry acid
None of these
Arrhenius acid
Arrhenius acid
There are three main definitions for acids and bases: the Lewis acids and bases, Bronsted-Lowry acids and bases, and Arrhenius acids and bases.
A Lewis acid is a species which can accept an electron pair from a donor. An example of a Lewis acid is 

A Bronsted-Lowry acid is a species which can donate a proton. An example of a Bronsted-Lowry acid is 

An Arrhenius acid is a species which releases hydrogen ions into solution. An example of an Arrhenius acid is 





Example Question #4 : Lewis, Brønsted Lowry, And Arrhenius Definitions
What is the pH of a 

PH is defined as 


=
Example Question #171 : College Chemistry
According to the Brønsted-Lowry definition of acids and bases, which species in the reaction are acids?
There are no acids in the reaction
Remember a Brønsted-Lowry acid is defined as a proton donor.
In the forward reaction, 

The acids in this reaction are 

All College Chemistry Resources