All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Triangles
What is the perimeter of an isosceles triangle given that the sides 5 units long and half of the base measures to 4 units?
The base of the triangle is 4 + 4 = 8 so the total perimeter is 5 + 5 + 8 = 18.
Example Question #51 : Geometry
An acute Isosceles triangle has two sides with length 
. The length of side










This Isosceles triangle has two sides with a length of 
To find the missing side, double the value of side 


Therefore, this triangle has two sides with lengths of 

To find the perimeter, apply the formula: 

Example Question #57 : Geometry
An acute Isosceles triangle has two sides with length 
. The length of side




To solve this problem apply the formula: 
However, first calculate the length of the missing side by: 
Thus, the solution is:
Example Question #58 : Geometry
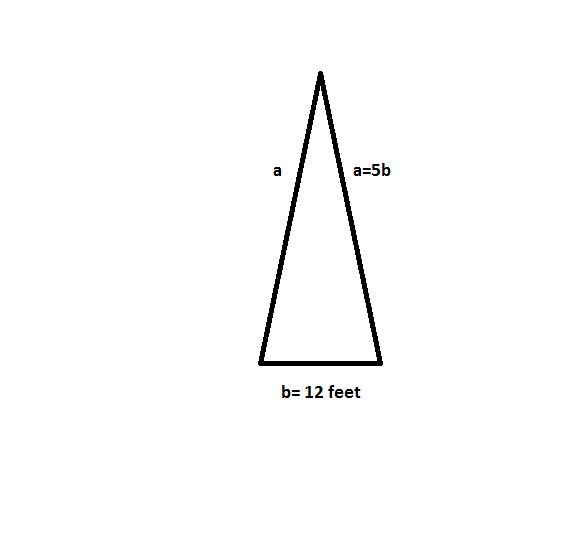
Find the perimeter of the acute Isosceles triangle shown above.
To solve this problem apply the formula: 
However, first calculate the length of the missing side by:
Example Question #1251 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning
An obtuse Isosceles triangle has two sides with length 
. The length of side









By definition, an Isosceles triangle must have two equivalent side lengths. Since we are told that 







Now, apply the formula: 
Then, simplify the fraction/convert to mixed number fraction:
Example Question #60 : Geometry
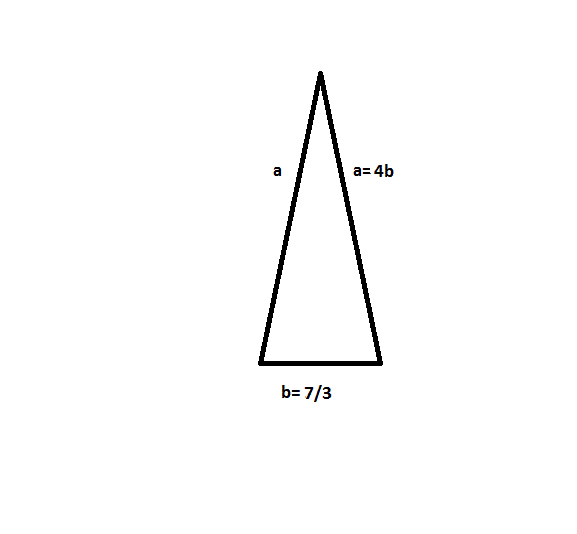
Find the perimeter of the acute Isosceles triangle shown above.
In order to solve this problem, first find the length of the missing sides. Then apply the formula:
Each of the missing sides equal: 
Then apply the perimeter formula:
Example Question #1 : Triangles

An acute Isosceles triangle has two sides with length 
. The length of side



![\sqrt[3]{a}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/334904/gif.latex)





In order to solve this problem, first find the length of the missing sides. Then apply the formula:
The missing side equals:
Then plug each side length into the perimeter formula:
Example Question #2 : Triangles

An acute Isosceles triangle has two sides with length 
. The length of side









In order to solve this problem, first find the length of the missing sides. Then apply the formula:
The missing side equals:
Then, apply the perimeter formula by plugging in the side values:
Example Question #3 : Triangles
An acute Isosceles triangle has two sides with length 
. The length of side









To solve this problem apply the formula: 
However, first calculate the length of the missing side by:

Since, it takes 

Example Question #4 : Triangles
An acute Isosceles triangle has two sides with length 
. The length of side










To find the perimeter of this triangle, apply the formula:
Note: Since this is an acute Isosceles triangle, the length of the base must be smaller than the length of both of the equivalent sides.
All GRE Math Resources



























![b=\sqrt[3]{a}=\sqrt[3]{8}=2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/334905/gif.latex)












