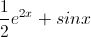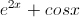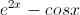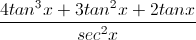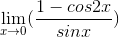All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Finding First And Second Derivatives
Find the second derivative of f(x).
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
First we should find the first derivative of 




The second derivative is just the derivative of the first derivative:
Example Question #22 : Calculus Ii — Integrals
Find the derivative of the function

Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
We can use the Chain Rule:
Let 

Example Question #1 : Derivatives
Evaluate the following limit:
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
When 



All High School Math Resources
Popular Subjects
Chemistry Tutors in Dallas Fort Worth, Calculus Tutors in Houston, Biology Tutors in New York City, GRE Tutors in Chicago, ISEE Tutors in Miami, English Tutors in New York City, MCAT Tutors in Phoenix, Reading Tutors in New York City, ACT Tutors in New York City, GRE Tutors in Washington DC
Popular Courses & Classes
GRE Courses & Classes in Denver, ISEE Courses & Classes in Los Angeles, LSAT Courses & Classes in Boston, GRE Courses & Classes in Philadelphia, ACT Courses & Classes in Houston, LSAT Courses & Classes in Miami, ISEE Courses & Classes in San Diego, Spanish Courses & Classes in Houston, GMAT Courses & Classes in Phoenix, GRE Courses & Classes in Dallas Fort Worth