All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Radicals
Simplify the expression. Find the positive solution only.
When working in square roots, each component can be treated separately.
Now, we can simplify each term.
Combine the simplified terms to find the answer. Anything outside of the square root is combined, while anything under the root is combined under the root.
Example Question #1 : Understanding Radicals
Convert the radical to exponential notation.
Remember that any term outside the radical will be in the denominator of the exponent.
Since 
Example Question #2 : Understanding Radicals
What is the value of 
9
243
27
2.41
3
243
An exponent written as a fraction can be rewritten using roots. 
![\sqrt[2]{9^5}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/92839/gif.latex)
![\sqrt[2]{9^5}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/121574/gif.latex)
![(\sqrt[2]{9})^{5}=3^{5}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/92840/gif.latex)
Example Question #1 : Radicals
Express the following radical in rational (exponential) form:
To convert the radical to exponent form, begin by converting the integer:

Now, divide each exponent by 
Finally, simplify the exponents:
Example Question #52 : Algebra Ii
Express the following radical in rational (exponential) form:
To convert the radical to exponent form, begin by converting the integer:
Now, divide each exponent by 
Finally, simplify the exponents:
Example Question #2 : Radicals
Which fraction is equivalent to 
Multiply the numerator and denominator by the compliment of the denominator:
Simplify the expression:
Example Question #3 : Understanding Radicals
Simplify the following radical. Express in rational (exponential) form.
Multiply the numerator and denominator by the compliment of the denominator:
Simplify the expression:
Example Question #3 : Radicals
Choose the fraction equivalent to 
Multiply the numerator and denominator by the compliment of the denominator:

Simplify the expression:
Example Question #9 : Understanding Radicals
Simplify the following radical. Express in rational (exponential) form.
Multiply the numerator and denominator to the exponent:
Simplify the expression by combining like terms:
Example Question #10 : Understanding Radicals
Express the following radical in rational (exponential) form:
To convert the radical to exponent form, begin by converting the integer:
Now, divide each exponent by 
Finally, simplify the exponents:
All High School Math Resources



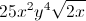






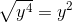

![\small \sqrt[4]{13}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/116532/gif.latex)




![\sqrt[b]{x^a}=x^{\frac{a}{b}}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/88790/gif.latex)
![\sqrt[4]{13}=13^{\frac{1}{4}}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/88791/gif.latex)









![\sqrt[4]{96a^5b^7c^8}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/152426/gif.latex)





![\sqrt[4]{96a^5b^7c^8}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/152427/gif.latex)
![=\sqrt[4]{3\cdot 2^5a^5b^7c^8}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/152734/gif.latex)




























![\sqrt[3]{16x^5y^6z^8}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/152387/gif.latex)





![\sqrt[3]{16x^5y^6z^8}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/152388/gif.latex)
![=\sqrt[3]{2^4x^5y^6z^8}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/152731/gif.latex)





