All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Surface Area Of A Tetrahedron
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The surface area of a regular tetrahedron with edges of length 1
(b) 2
(a) and (b) are equal.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(a) is greater.
(b) is greater.
(b) is greater.
A regular tetrahedron has four faces, each of which is an equilateral triangle. Therefore, its surface area, given sidelength 

Substitute 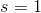

Example Question #1 : How To Find The Radius Of A Sphere
The volume of a sphere is one cubic yard. Give its radius in inches.
The volume 

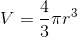
To find the radius in yards, we set 

![r = \sqrt[3]{ \frac{3}{4\pi} } = \sqrt[3]{ \frac{3\cdot 2 \pi^{2}}{4\pi \cdot 2 \pi^{2}} }= \sqrt[3]{ \frac{6 \pi^{2}}{8 \pi^{3}} } = \frac{ \sqrt[3]{6 \pi^{2}} } {2\pi}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/203839/gif.latex)
Since the problem requests the radius in inches, multiply by 36:
Example Question #331 : Geometry
In terms of 
36 inches = 



Example Question #31 : Solid Geometry
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The volume of a sphere with radius
(b) The volume of a cube with sidelength
(a) and (b) are equal
(a) is greater
(b) is greater
It is impossible to tell from the information given
(b) is greater
A sphere with radius 


Example Question #1 : How To Find The Volume Of A Sphere
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The volume of a cube with sidelength inches.
(b) The volume of a sphere with radius inches.
(a) is greater.
(b) is greater.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(a) and (b) are equal.
(a) is greater.
You do not need to calculate the volumes of the figures. All you need to do is observe that a sphere with radius inches has diameter
inches, and can therefore be inscribed inside the cube with sidelength
inches. This give the cube larger volume, making (a) the greater quantity.
Example Question #32 : Solid Geometry
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The volume of a sphere with diameter one foot
(b)
(b) is greater.
(a) and (b) are equal.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(a) is greater.
(a) is greater.
The radius of the sphere is one half of its diameter of one foot, which is six inches, so substitute 

which is greater than 
Example Question #33 : Solid Geometry

(A) The volume of a cube with edges of length
(B) The volume of a sphere with radius
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(B) is greater
(A) and (B) are equal
(A) is greater
(A) is greater
No calculation is really needed here, as a sphere with radius 


Example Question #7 : Spheres
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The radius of a sphere with surface area
(b) The radius of a sphere with volume
(a) is the greater quantity
It cannot be determined which of (a) and (b) is greater
(a) and (b) are equal
(b) is the greater quantity
(a) and (b) are equal
The formula for the surface area of a sphere, given its radius 
The sphere in (a) has surface area 
The formula for the volume of a sphere, given its radius 
The sphere in (b) has volume 
The radius of both spheres is 3.
Example Question #6 : Spheres
In terms of 




Example Question #1 : How To Find The Surface Area Of A Sphere
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The surface area of a sphere with radius 1
(b) 12
(b) is greater.
(a) and (b) are equal.
(a) is greater.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(a) is greater.
The surface area of a sphere can be found using the formula

The surface area of the given sphere can be found by substituting 


This makes (a) greater.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources



![\frac{ 18\sqrt[3]{6 \pi^{2}} } {\pi} \textrm{ in}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/203814/gif.latex)

![\frac{ 6\sqrt[3]{6 \pi^{2}} } {\pi} \textrm{ in}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/203816/gif.latex)
![\frac{ \sqrt[3]{6 \pi^{2}} } {2\pi}\textrm{ in}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/203815/gif.latex)


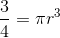


![36 \times \frac{ \sqrt[3]{6 \pi^{2}} } {2\pi} = \frac{ 18\sqrt[3]{6 \pi^{2}} } {\pi}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/203840/gif.latex)






























![r = \sqrt[3]{27} = 3](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/658471/gif.latex)














