All MCAT Physical Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #181 : Mcat Physical Sciences
At a local concert, a speaker is set up to produce low-pitched base sounds with a frequency range of 20Hz to 200Hz, which can be modeled as sine waves. In a simplified model, the sound waves the speaker produces can be modeled as a cylindrical pipe with one end closed that travel through the air at a velocity of 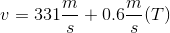
How long would it take for a 30Hz beat to reach an audience member 100m away when the ambient temperature is 21ºC?
0.91s
0.31s
0.11s
0.29s
0.29s
The question asks us to determine how long it will take for a wave beat to reach an audience member at 100m away; thus, we need to calculate the velocity of the wave to determine the time.
We know from kinematics that 

Example Question #182 : Mcat Physical Sciences
A wave produced on a string travels with a velocity of 
The velocity of a wave can be obtained with the formula 


Let's assume that a string with tension 


If we increase the tension by a factor of four, we will get the below expression.
We can see that 

Example Question #1 : Velocity And Waves
Through which of the following would you expect a photon to travel fastest?
Water
Air
Glass
Vacuum
Vacuum
A photon will travel fastest through a vacuum. Photons are generally massless and can be thought of as a light wave, which travels fastest in a vacuum and slowest through a metal or solid. This can be visualized using the concept of the index of refraction, which describes the speed of light through air compared to the speed through other mediums. A vacuum will be the least dense and cause the least hindrance to a photon as it travels, thus giving it the lowest index of refraction and allowing the fastest speed of light.
Example Question #1 : Velocity And Waves
You are out snorkling off the coast of an exotic island when a pod of whales comes swimming by. The pod is 100m away. If they emit sounds underwater with an average frequency of 2200Hz and there are 500 complete sound waves between you and the pod, how fast is the speed of sound in the water?
If there are 500 waves over a distance of 100 meters, we can say that the wavelength is:
Now we can use the formula for the speed of waves:
Example Question #21 : General Principles And Properties
Which statement is not true for all waves?
Their speed depends on the temperature of the transmitting medium
They can be diffracted
Wavelength is the distance between corresponding points on successive cycles
They can produce interference
Their speed depends on the temperature of the transmitting medium
The speed of sound is dependent on the temperature of the transmitting medium. The speed of light is not.
Example Question #1 : Mirrors And Lenses
A virtual image is formed 

Use the equation:
Focal length is negative for convex mirrors, and image distance is negative for virtual images. We are given these values in the question, allowing us to calculate the object distance.
Example Question #2 : Mirrors And Lenses
How far from a converging lens must an object be placed to produce an image that is NOT real and inverted? Given the answer as 

When an object is placed a distance from a converging lens or mirror that is equal to the focal length, no image is produced. To test this out, stand in front of a single concave mirror and continue to back up until you no longer see an image. Once you've reached this point, you will be standing one focal length away from the mirror.
When the object is less than one focal length away from the converging lens/mirror, the image will be virtual and upright.
If you don't have these trends committed to memory, you can derive them from the equation 
When 
Example Question #3 : Mirrors And Lenses
A certain farsighted person cannot focus on objects closer to his eyes than 


First we need the object and image distances away from the eyeglass lenses. Here, the newspaper is the object and the 
Now apply the thin lens equation to determine focal length.
Recall that if the image is on the same side of the lens as the object, then image distance is negative.
Example Question #1 : Mirrors And Lenses
An object is placed 50cm in front of a concave mirror of radius 60cm. How far from the mirror is the image?
Relevant equations:
Step 1: Find the focal length of the mirror.
Step 2: Plug this focal length and the object distance into the lens equation.
Example Question #2 : Optics
An object that is 3cm tall is placed 30cm from a convex spherical mirror of radius 40cm, along its central axis. What is the height of the image that is formed?
Relevant equations:
Step 1: Find the focal length of the mirror (remembering that convex mirrors have negative focal lengths, by convention).
Step 2: Find the image distance using the thin lens equation.
Step 3: Use the magnification equation to relate the object distances and heights.
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Physical Resources







































































